Page 92 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 92
2.3 3D MARINE SEISMIC ACQUISITION 83
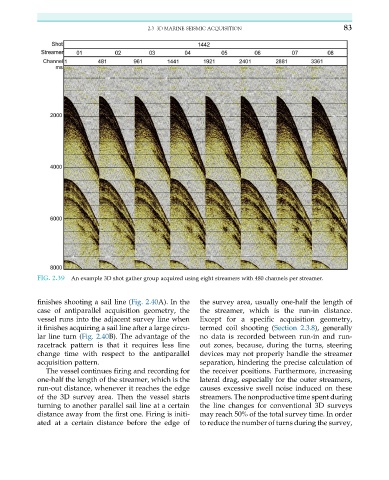
FIG. 2.39 An example 3D shot gather group acquired using eight streamers with 480 channels per streamer.
finishes shooting a sail line (Fig. 2.40A). In the the survey area, usually one-half the length of
case of antiparallel acquisition geometry, the the streamer, which is the run-in distance.
vessel runs into the adjacent survey line when Except for a specific acquisition geometry,
it finishes acquiring a sail line after a large circu- termed coil shooting (Section 2.3.8), generally
lar line turn (Fig. 2.40B). The advantage of the no data is recorded between run-in and run-
racetrack pattern is that it requires less line out zones, because, during the turns, steering
change time with respect to the antiparallel devices may not properly handle the streamer
acquisition pattern. separation, hindering the precise calculation of
The vessel continues firing and recording for the receiver positions. Furthermore, increasing
one-half the length of the streamer, which is the lateral drag, especially for the outer streamers,
run-out distance, whenever it reaches the edge causes excessive swell noise induced on these
of the 3D survey area. Then the vessel starts streamers. The nonproductive time spent during
turning to another parallel sail line at a certain the line changes for conventional 3D surveys
distance away from the first one. Firing is initi- may reach 50% of the total survey time. In order
ated at a certain distance before the edge of to reduce the number of turns during the survey,