Page 299 - Adaptive Identification and Control of Uncertain Systems with Nonsmooth Dynamics
P. 299
302 Adaptive Identification and Control of Uncertain Systems with Non-smooth Dynamics
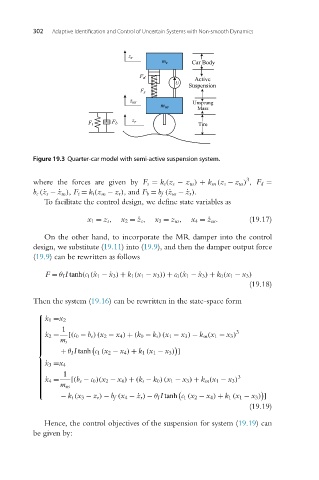
Figure 19.3 Quarter-car model with semi-active suspension system.
3
where the forces are given by F s = k s (z s − z us ) + k sn (z s − z us ) , F d =
b e (˙ z s −¨z us ), F t = k t (z us − z r ),and F b = b f (˙ z us −¨z r ).
To facilitate the control design, we define state variables as
x 1 = z s , x 2 =˙z s , x 3 = z us , x 4 =˙z us . (19.17)
On the other hand, to incorporate the MR damper into the control
design, we substitute (19.11)into(19.9), and then the damper output force
(19.9)can be rewrittenasfollows
F = θ I I tanh(c 1 (˙x 1 −¨x 3 ) + k 1 (x 1 − x 3 )) + c 0 (˙x 1 −¨x 3 ) + k 0 (x 1 − x 3 )
(19.18)
Then the system (19.16) can be rewritten in the state-space form
⎧
⎪ ˙ x 1 =x 2
⎪
1
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪ 3
⎪ ˙x 2 = [(c 0 − b e )(x 2 − x 4 ) + (k 0 − k s )(x 1 − x 3 ) − k sn (x 1 − x 3 )
⎪
m s
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
+ θ I I tanh c 1 (x 2 − x 4 ) + k 1 (x 1 − x 3 ) ]
⎨
⎪ ˙ x 3 =x 4
⎪
⎪
1
⎪
⎪
⎪ 3
⎪
⎪ ˙x 4 = [(b e − c 0 )(x 2 − x 4 ) + (k s − k 0 )(x 1 − x 3 ) + k sn (x 1 − x 3 )
⎪
m us
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎪
⎩
− k t (x 3 − z r ) − b f (x 4 −¨z r ) − θ I I tanh c 1 (x 2 − x 4 ) + k 1 (x 1 − x 3 ) ]
(19.19)
Hence, the control objectives of the suspension for system (19.19)can
be given by: