Page 182 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 182
ZEOLITES AND MOLECULAR SIEVES: SYNTHESIS AND MOLECULAR SIEVING PROPERTIES 167
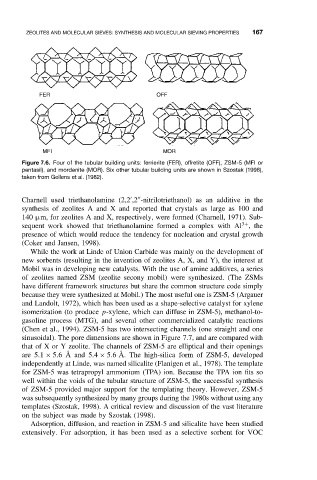
FER OFF
MFI MOR
Figure 7.6. Four of the tubular building units: ferrierite (FER), offretite (OFF), ZSM-5 (MFI or
pentasil), and mordenite (MOR). Six other tubular building units are shown in Szostak (1998),
taken from Gellens et al. (1982).
Charnell used triethanolamine (2,2 ,2 -nitrilotriethanol) as an additive in the
synthesis of zeolites A and X and reported that crystals as large as 100 and
140 µm, for zeolites A and X, respectively, were formed (Charnell, 1971). Sub-
sequent work showed that triethanolamine formed a complex with Al ,the
3+
presence of which would reduce the tendency for nucleation and crystal growth
(Coker and Jansen, 1998).
While the work at Linde of Union Carbide was mainly on the development of
new sorbents (resulting in the invention of zeolites A, X, and Y), the interest at
Mobil was in developing new catalysts. With the use of amine additives, a series
of zeolites named ZSM (zeolite secony mobil) were synthesized. (The ZSMs
have different framework structures but share the common structure code simply
because they were synthesized at Mobil.) The most useful one is ZSM-5 (Argauer
and Landolt, 1972), which has been used as a shape-selective catalyst for xylene
isomerization (to produce p-xylene, which can diffuse in ZSM-5), methanol-to-
gasoline process (MTG), and several other commercialized catalytic reactions
(Chen et al., 1994). ZSM-5 has two intersecting channels (one straight and one
sinusoidal). The pore dimensions are shown in Figure 7.7, and are compared with
that of X or Y zeolite. The channels of ZSM-5 are elliptical and their openings
are 5.1 × 5.6 ˚ Aand 5.4 × 5.6 ˚ A. The high-silica form of ZSM-5, developed
independently at Linde, was named silicalite (Flanigen et al., 1978). The template
for ZSM-5 was tetrapropyl ammonium (TPA) ion. Because the TPA ion fits so
well within the voids of the tubular structure of ZSM-5, the successful synthesis
of ZSM-5 provided major support for the templating theory. However, ZSM-5
was subsequently synthesized by many groups during the 1980s without using any
templates (Szostak, 1998). A critical review and discussion of the vast literature
on the subject was made by Szostak (1998).
Adsorption, diffusion, and reaction in ZSM-5 and silicalite have been studied
extensively. For adsorption, it has been used as a selective sorbent for VOC