Page 178 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 178
ZEOLITE TYPESA,X,AND Y 163
such as fuel tank purging in military airplanes, where pressurized air is readily
available as the feed. A potentially useful approach for kinetic separation is to
use partially ion-exchanged zeolites, that is, zeolites with mixed cations. For
example, the diffusivities of CH 4 ,C 2 H 6 ,and CO 2 in 4A zeolite can be reduced
to desired values by partial exchange of Na with K to decrease the aperture
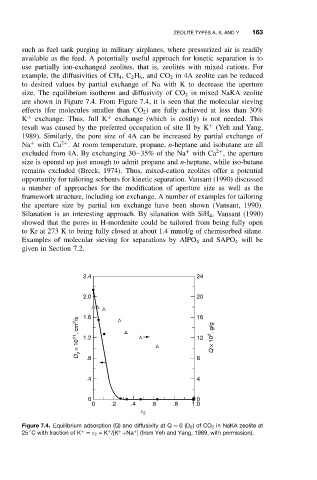
size. The equilibrium isotherm and diffusivity of CO 2 in mixed NaKA zeolite
are shown in Figure 7.4. From Figure 7.4, it is seen that the molecular sieving
effects (for molecules smaller than CO 2 ) are fully achieved at less than 30%
K + exchange. Thus, full K + exchange (which is costly) is not needed. This
+
result was caused by the preferred occupation of site II by K (Yeh and Yang,
1989). Similarly, the pore size of 4A can be increased by partial exchange of
+
2+
Na with Ca . At room temperature, propane, n-heptane and isobutane are all
2+
+
excluded from 4A. By exchanging 30–35% of the Na with Ca ,the aperture
size is opened up just enough to admit propane and n-heptane, while iso-butane
remains excluded (Breck, 1974). Thus, mixed-cation zeolites offer a potential
opportunity for tailoring sorbents for kinetic separation. Vansant (1990) discussed
a number of approaches for the modification of aperture size as well as the
framework structure, including ion exchange. A number of examples for tailoring
the aperture size by partial ion exchange have been shown (Vansant, 1990).
Silanation is an interesting approach. By silanation with SiH 4 , Vansant (1990)
showed that the pores in H-mordenite could be tailored from being fully open
to Kr at 273 K to being fully closed at about 1.4 mmol/g of chemisorbed silane.
Examples of molecular sieving for separations by AlPO 4 and SAPO 4 will be
given in Section 7.2.
2.4 24
2.0 20
× 10 11 , cm 2 /s 1.6 16 × 10 2 , g/g
12
1.2
D o .8 8 Q
.4 4
0 0 0
0 .2 .4 .6 .8 1.0
e 2
Figure 7.4. Equilibrium adsorption (Q) and diffusivity at Q = 0(D 0 )of CO 2 in NaKA zeolite at
◦
+
+
+
+
25 C with fraction of K = ε 2 =K /[K +Na ] (from Yeh and Yang, 1989, with permission).