Page 181 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 181
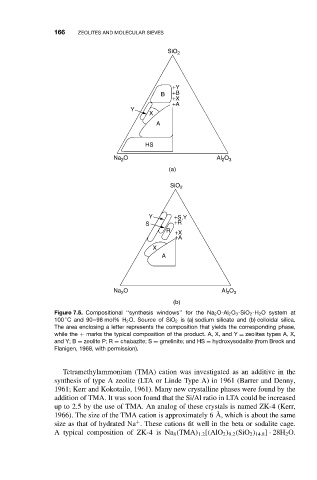
166 ZEOLITES AND MOLECULAR SIEVES
SiO 2
+Y
B +B
+X
+A
Y
X
A
HS
Na O Al O 3
2
2
(a)
SiO
2
Y +S,Y
S +R
R +X
+A
X
A
Na O Al O 3
2
2
(b)
Figure 7.5. Compositional ‘‘synthesis windows’’ for the Na 2 O-Al 2 O 3 -SiO 2 -H 2 O system at
◦
100 C and 90–98 mol% H 2 O. Source of SiO 2 is (a) sodium silicate and (b) colloidal silica.
The area enclosing a letter represents the composition that yields the corresponding phase,
while the + marks the typical composition of the product. A, X, and Y = zeolites types A, X,
and Y; B = zeolite P; R = chabazite; S = gmelinite; and HS = hydroxysodalite (from Breck and
Flanigen, 1968, with permission).
Tetramethylammonium (TMA) cation was investigated as an additive in the
synthesis of type A zeolite (LTA or Linde Type A) in 1961 (Barrer and Denny,
1961; Kerr and Kokotailo, 1961). Many new crystalline phases were found by the
addition of TMA. It was soon found that the Si/Al ratio in LTA could be increased
up to 2.5 by the use of TMA. An analog of these crystals is named ZK-4 (Kerr,
1966). The size of the TMA cation is approximately 6 ˚ A, which is about the same
size as that of hydrated Na . These cations fit well in the beta or sodalite cage.
+
A typical composition of ZK-4 is Na 8 (TMA) 1.2 [(AlO 2 ) 9.2 (SiO 2 ) 14.8 ] · 28H 2 O.