Page 384 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 384
NO X REMOVAL 369
100
a
80 b
c
d
e
NO Removal (%) 40
60
20
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
Time (h)
◦
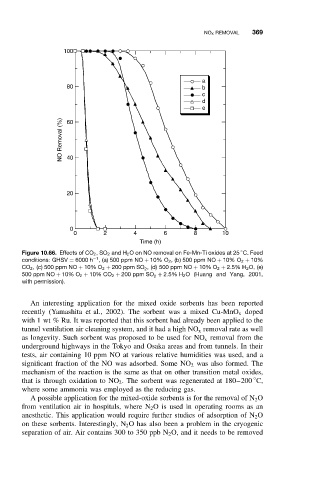
Figure 10.66. Effects of CO 2 ,SO 2 and H 2 O on NO removal on Fe-Mn-Ti oxides at 25 C. Feed
conditions: GHSV = 6000 h −1 , (a) 500 ppm NO + 10% O 2 , (b) 500 ppm NO + 10% O 2 + 10%
CO 2 , (c) 500 ppm NO + 10% O 2 + 200 ppm SO 2 , (d) 500 ppm NO + 10% O 2 + 2.5% H 2 O, (e)
500 ppm NO + 10% O 2 + 10% CO 2 + 200 ppm SO 2 + 2.5% H 2 O (Huang and Yang, 2001,
with permission).
An interesting application for the mixed oxide sorbents has been reported
recently (Yamashita et al., 2002). The sorbent was a mixed Cu-MnO x doped
with 1 wt % Ru. It was reported that this sorbent had already been applied to the
tunnel ventilation air cleaning system, and it had a high NO x removal rate as well
as longevity. Such sorbent was proposed to be used for NO x removal from the
underground highways in the Tokyo and Osaka areas and from tunnels. In their
tests, air containing 10 ppm NO at various relative humidities was used, and a
significant fraction of the NO was adsorbed. Some NO 2 was also formed. The
mechanism of the reaction is the same as that on other transition metal oxides,
◦
that is through oxidation to NO 2 . The sorbent was regenerated at 180–200 C,
where some ammonia was employed as the reducing gas.
A possible application for the mixed-oxide sorbents is for the removal of N 2 O
from ventilation air in hospitals, where N 2 O is used in operating rooms as an
anesthetic. This application would require further studies of adsorption of N 2 O
on these sorbents. Interestingly, N 2 O has also been a problem in the cryogenic
separation of air. Air contains 300 to 350 ppb N 2 O, and it needs to be removed