Page 386 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 386
REFERENCES 371
18
NO x Adsorption/desorption amount (mg/g sorbent)
16
14
12
10
8
6
[NO] = 1000 ppm
4 [O ] = 4%
2
Adsorption at 200°C
2 Desorption at 450°C
Data of Eguchi et al.
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160
Time (minute)
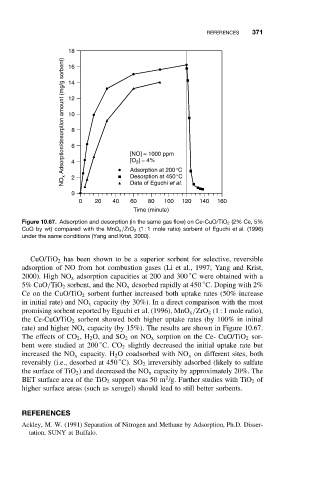
Figure 10.67. Adsorption and desorption (in the same gas flow) on Ce-CuO/TiO 2 (2% Ce, 5%
CuO by wt) compared with the MnO x /ZrO 2 (1 : 1 mole ratio) sorbent of Eguchi et al. (1996)
under the same conditions (Yang and Krist, 2000).
CuO/TiO 2 has been shown to be a superior sorbent for selective, reversible
adsorption of NO from hot combustion gases (Li et al., 1997; Yang and Krist,
◦
2000). High NO x adsorption capacities at 200 and 300 C were obtained with a
◦
5% CuO/TiO 2 sorbent, and the NO x desorbed rapidly at 450 C. Doping with 2%
Ce on the CuO/TiO 2 sorbent further increased both uptake rates (50% increase
in initial rate) and NO x capacity (by 30%). In a direct comparison with the most
promising sorbent reported by Eguchi et al. (1996), MnO x /ZrO 2 (1 : 1 mole ratio),
the Ce-CuO/TiO 2 sorbent showed both higher uptake rates (by 100% in initial
rate) and higher NO x capacity (by 15%). The results are shown in Figure 10.67.
The effects of CO 2 ,H 2 O, and SO 2 on NO x sorption on the Ce- CuO/TiO 2 sor-
◦
bent were studied at 200 C. CO 2 slightly decreased the initial uptake rate but
increased the NO x capacity. H 2 O coadsorbed with NO x on different sites, both
◦
reversibly (i.e., desorbed at 450 C). SO 2 irreversibly adsorbed (likely to sulfate
the surface of TiO 2 ) and decreased the NO x capacity by approximately 20%. The
2
BET surface area of the TiO 2 support was 50 m /g. Further studies with TiO 2 of
higher surface areas (such as xerogel) should lead to still better sorbents.
REFERENCES
Ackley, M. W. (1991) Separation of Nitrogen and Methane by Adsorption, Ph.D. Disser-
tation, SUNY at Buffalo.