Page 12 - Adsorption Technology & Design, Elsevier (1998)
P. 12
Adsorbents 9
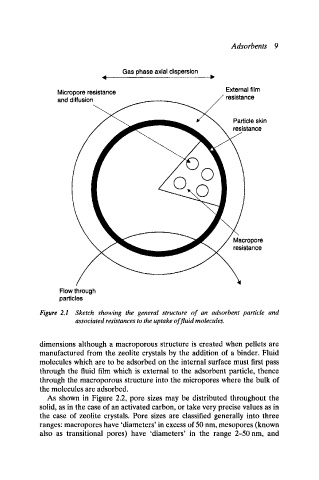
Gas phase axial dispersion
Micropore resistance External film
and diffusion ~ ~ resistance
Particle skin
resistance
Macropore
resistance
Flow through
particles
Figure 2.1 Sketch showing the general structure of an adsorbent particle and
associated resistances to the uptake of fluid molecules.
dimensions although a macroporous structure is created when pellets are
manufactured from the zeolite crystals by the addition of a binder. Fluid
molecules which are to be adsorbed on the internal surface must first pass
through the fluid film which is external to the adsorbent particle, thence
through the macroporous structure into the micropores where the bulk of
the molecules are adsorbed.
As shown in Figure 2.2, pore sizes may be distributed throughout the
solid, as in the case of an activated carbon, or take very precise values as in
the case of zeolite crystals. Pore sizes are classified generally into three
ranges: macropores have 'diameters' in excess of 50 nm, mesopores (known
also as transitional pores) have 'diameters' in the range 2-50nm, and