Page 124 - Adsorption, Ion Exchange & Catalysis- 2007, Elsevier - Copy
P. 124
Else_AIEC-INGLE_cH003.qxd 7/13/2006 1:45 PM Page 120
120 3. Heterogeneous Processes and Reactor Analysis
0.35
0.3
0.25
0.2
0.15
gas holdup
0.1
0.05
hG
hG,f
0
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25
u sL /u sG
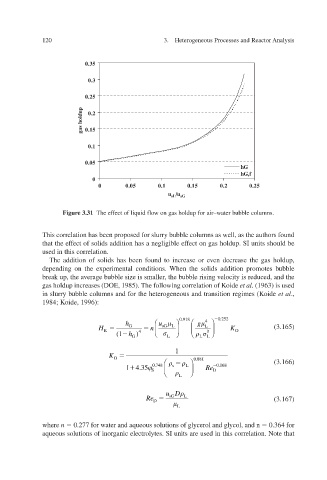
Figure 3.31 The effect of liquid flow on gas holdup for air–water bubble columns.
This correlation has been proposed for slurry bubble columns as well, as the authors found
that the effect of solids addition has a negligible effect on gas holdup. SI units should be
used in this correlation.
The addition of solids has been found to increase or een decrease the gas holdup,
v
depending on the experimental conditions. When the solids addition promotes b ubble
erage b
,
v
break up, the aubble size is smaller the bubble rising velocity is reduced, and the
gas holdup increases (DOE, 1985). The follo wing correlation of Koide et al . (1963) is used
in slurry bubble columns and for the heterogeneous and transition regimes (K oide et al .,
1984; Koide, 1996):
4
h G u sG L
0.918 g
0.252
L
H K n 3 K O (3.165)
(1 h ) G 4
L
L
L
1
K O 0.881
1 4.35 0.748 s L Re 0.168 (3.166)
S L D
uD sG L
Re (3.167)
D
L
where n 0.277 for w and n ater and aqueous solutions of glycerol and glycol, 0.364 for
aqueous solutions of inorganic electrolytes. SI units are used in this correlation. Note that