Page 174 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 174
Advanced gas turbine cycles
+ pjq
CLOSED T CYCLE
CYCLE
IL
COOLER v
A
3,
\ SEMI-CLOSED ’+
CYCLE T
COOLER 1r
+
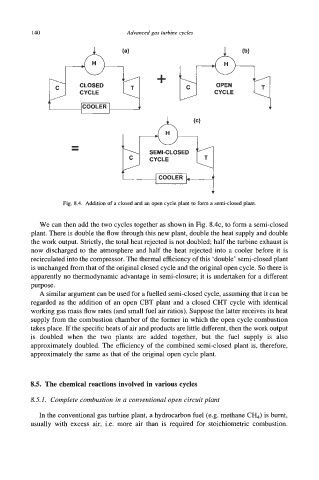
Fig. 8.4. Addition of a closed and an open cycle plant to form a semiclosed plant.
We can then add the two cycles together as shown in Fig. SAC, to form a semi-closed
plant. There is double the flow through this new plant, double the heat supply and double
the work output. Strictly, the total heat rejected is not doubled; half the turbine exhaust is
now discharged to the atmosphere and half the heat rejected into a cooler before it is
recirculated into the compressor. The thermal efficiency of this ‘double’ semi-closed plant
is unchanged from that of the original closed cycle and the original open cycle. So there is
apparently no thermodynamic advantage in semi-closure; it is undertaken for a different
purpose.
A similar argument can be used for a fuelled semi-closed cycle, assuming that it can be
regarded as the addition of an open CBT plant and a closed CHT cycle with identical
working gas mass flow rates (and small fuel air ratios). Suppose the latter receives its heat
supply from the combustion chamber of the former in which the open cycle combustion
takes place. If the specific heats of air and products are little different, then the work output
is doubled when the two plants are added together, but the fuel supply is also
approximately doubled. The efficiency of the combined semi-closed plant is, therefore,
approximately the same as that of the original open cycle plant.
8.5. The chemical reactions involved in various cycles
8.5.1. Complete combustion in a conventional open circuit plans
In the conventional gas turbine plant, a hydrocarbon fuel (e.g. methane CI&) is burnt,
usually with excess air, i.e. more air than is required for stoichiometric combustion.