Page 192 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 192
158 Advanced gas turbine cycles
Their calculations show remarkably high overall efficiency, ranging from 56% at 1300 K
to over 64% at 1500 K (with r between 20 and 25).
8.6.4.2. Plants with combustion modifcation (full oxidation)
A number of plants have been proposed in which pure oxygen is used for combustion,
usually in combination with the concept of cycle semi-closure.
CBT ana' CCGT plants with full oxidation (04, 05). We next consider two semi-closed
cycles for C02 removal (Cycles D4 and D5) with air replaced as the oxidant for the fuel,
by pure oxygen supplied from an additional plant.
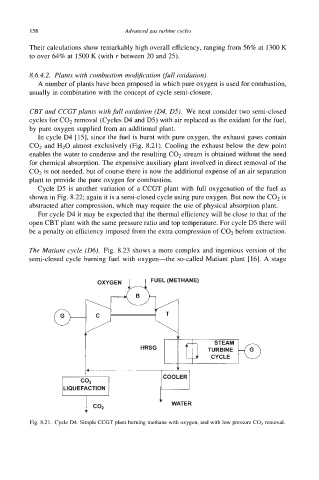
In cycle D4 [ 151, since the fuel is burnt with pure oxygen, the exhaust gases contain
C02 and H20 almost exclusively (Fig. 8.21). Cooling the exhaust below the dew point
enables the water to condense and the resulting COz stream is obtained without the need
for chemical absorption. The expensive auxiliary plant involved in direct removal of the
COz is not needed, but of course there is now the additional expense of an air separation
plant to provide the pure oxygen for combustion.
Cycle D5 is another variation of a CCGT plant with full oxygenation of the fuel as
shown in Fig. 8.22; again it is a semi-closed cycle using pure oxygen. But now the C02 is
abstracted after compression, which may require the use of physical absorption plant.
For cycle D4 it may be expected that the thermal efficiency will be close to that of the
open CBT plant with the same pressure ratio and top temperature. For cycle D5 there will
be a penalty on efficiency imposed from the extra compression of COz before extraction.
The Matiant cycle (06). Fig. 8.23 shows a more complex and ingenious version of the
semi-closed cycle burning fuel with oxygen-the so-called Matiant plant [ 161. A stage
FUEL (METHANE)
T
LIQUEFACTION
WATER
Fig. 8.21. Cycle D4. Simple CCGT plant burning methane with oxygen, and with low pressure COz removal.