Page 220 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 220
200 2.5.4. Enantioselective Dihydroxylation of Alkenes
CHAPTER 2 Osmium tetroxide is a stereospecific oxidant that produces diols from alkenes
Stereochemistry, by a syn-addition. 162 Currently, the reaction is carried out using a catalytic amount
Conformation, of OsO , with a stoichiometric oxidant such as t-butyl hydroperoxide, 163 potassium
and Stereoselectivity 4
ferricyanide, 164 or morpholine-N-oxide. 165 Osmium tetroxide oxidations can be highly
enantioselective in the presence of chiral ligands. The most highly developed ligands
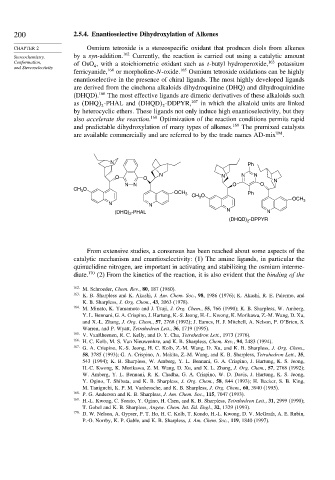
are derived from the cinchona alkaloids dihydroquinine (DHQ) and dihydroquinidine
(DHQD). 166 The most effective ligands are dimeric derivatives of these alkaloids such
as DHQ -PHAL and DHQD -DDPYR, 167 in which the alkaloid units are linked
2
2
by heterocyclic ethers. These ligands not only induce high enantioselectivity, but they
also accelerate the reaction. 168 Optimization of the reaction conditions permits rapid
and predictable dihydroxylation of many types of alkenes. 169 The premixed catalysts
are available commercially and are referred to by the trade names AD-mix TM .
N Ph
N N N N
O O N
NN O O
CH O OCH 3 CH O Ph
3
N N 3 OCH 3
N
(DHQ) -PHAL N
2
-DPPYR
(DHQD) 2
From extensive studies, a consensus has been reached about some aspects of the
catalytic mechanism and enantioselectivity: (1) The amine ligands, in particular the
quinuclidine nitrogen, are important in activating and stabilizing the osmium interme-
diate. 170 (2) From the kinetics of the reaction, it is also evident that the binding of the
162
M. Schroeder, Chem. Rev., 80, 187 (1980).
163 K. B. Sharpless and K. Akashi, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 98, 1986 (1976); K. Akashi, R. E. Palermo, and
K. B. Sharpless, J. Org. Chem., 43, 2063 (1978).
164 M. Minato, K. Yamamoto and J. Tsuji, J. Org. Chem., 55, 766 (1990); K. B. Sharpless, W. Amberg,
Y. L. Bennani, G. A. Crispino, J. Hartung, K.-S. Jeong, H.-L. Kwong, K. Morikawa, Z.-M. Wang, D. Xu,
and X.-L. Zhang, J. Org. Chem., 57, 2768 (1992); J. Eames, H. J. Mitchell, A. Nelson, P. O’Brien, S.
Warren, and P. Wyatt, Tetrahedron Lett., 36, 1719 (1995).
165
V. VanRheenen, R. C. Kelly, and D. Y. Cha, Tetrahedron Lett., 1973 (1976).
166 H. C. Kolb, M. S. Van Nieuwenhze, and K. B. Sharpless, Chem. Rev., 94, 2483 (1994).
167 G. A. Crispino, K.-S. Jeong, H. C. Kolb, Z.-M. Wang, D. Xu, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Org. Chem.,
58, 3785 (1993); G. A. Crispino, A. Makita, Z.-M. Wang, and K. B. Sharpless, Tetrahedron Lett., 35,
543 (1994); K. B. Sharpless, W. Amberg, Y. L. Bennani, G. A. Crispino, J. Hartung, K. S. Jeong,
H.-C. Kwong, K. Morikawa, Z. M. Wang, D. Xu, and X. L. Zhang, J. Org. Chem., 57, 2768 (1992);
W. Amberg, Y. L. Bennani, R. K. Chadha, G. A. Crispino, W. D. Davis, J. Hartung, K. S. Jeong,
Y. Ogino, T. Shibata, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Org. Chem., 58, 844 (1993); H. Becker, S. B. King,
M. Taniguchi, K. P. M. Vanhessche, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Org. Chem., 60, 3940 (1995).
168
P. G. Anderson and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 7047 (1993).
169 H.-L. Kwong, C. Sorato, Y. Ogino, H. Chen, and K. B. Sharpless, Tetrahedron Lett., 31, 2999 (1990);
T. Gobel and K. B. Sharpless, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 32, 1329 (1993).
170
D. W. Nelson, A. Gypser, P. T. Ho, H. C. Kolb, T. Kondo, H.-L. Kwong, D. V. McGrath, A. E. Rubin,
P.-O. Norrby, K. P. Gable, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 1840 (1997).