Page 217 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 217
the stoichiometric oxidant in combination with titanium catalysts. When enantiomer- 197
ically pure tartrate esters are included in the system, the reaction is highly enantio-
selective and is known as Sharpless asymmetric epoxidation. 156 Either the + or SECTION 2.5
− tartrate ester can be used, so either enantiomer of the desired product can be Enantioselective
Reactions
obtained. The allylic hydroxyl group serves to coordinate the reactant to titanium.
The mechanism involves exchange of the allylic alcohol and t-butyl hydroperoxide
for another ligand at the titanium atom. In the TS an oxygen atom from the peroxide
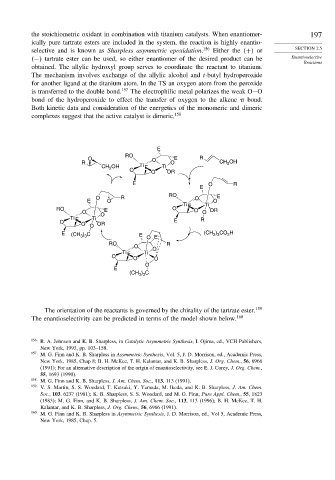
is transferred to the double bond. 157 The electrophilic metal polarizes the weak O−O
bond of the hydroperoxide to effect the transfer of oxygen to the alkene bond.
Both kinetic data and consideration of the energetics of the monomeric and dimeric
complexes suggest that the active catalyst is dimeric. 158
E
RO
O O E R
R O CH OH
2
CH OH Ti E Ti
2
O O OR
E O R
E
RO
O R O E
E O O
Ti E Ti
RO E O O OR
O O O
Ti E Ti R
O O O OR E
E (CH ) C E O E (CH ) CO H
2
3 3
3 3
RO R
O O
Ti E Ti
O O O
O
E
(CH ) C
3 3
The orientation of the reactants is governed by the chirality of the tartrate ester. 159
The enantioselectivity can be predicted in terms of the model shown below. 160
156 R. A. Johnson and K. B. Sharpless, in Catalytic Asymmetric Synthesis, I. Ojima, ed., VCH Publishers,
New York, 1993, pp. 103–158.
157
M. G. Finn and K. B. Sharpless in Asymmetric Synthesis, Vol. 5, J. D. Morrison, ed., Academic Press,
New York, 1985, Chap 8; B. H. McKee, T. H. Kalantar, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Org. Chem., 56, 6966
(1991); For an alternative description of the origin of enantioselectivity, see E. J. Corey, J. Org. Chem.,
55, 1693 (1990).
158 M. G. Finn and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 113 (1991).
159 V. S. Martin, S. S. Woodard, T. Katsuki, Y. Yamada, M. Ikeda, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem.
Soc., 103, 6237 (1981); K. B. Sharpless, S. S. Woodard, and M. G. Finn, Pure Appl. Chem., 55, 1823
(1983); M. G. Finn, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 113 (1996); B. H. McKee, T. H.
Kalantar, and K. B. Sharpless, J. Org. Chem., 56, 6966 (1991).
160
M. G. Finn and K. B. Sharpless in Asymmetric Synthesis, J. D. Morrison, ed., Vol 5, Academic Press,
New York, 1985, Chap. 5.