Page 212 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 212
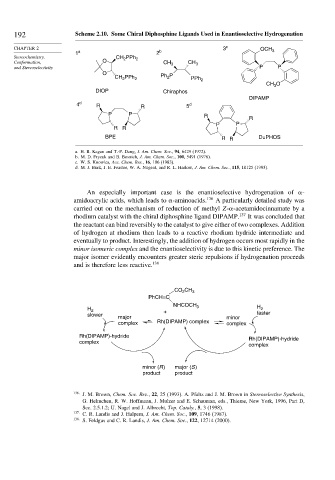
192 Scheme 2.10. Some Chiral Diphosphine Ligands Used in Enantioselective Hydrogenation
CHAPTER 2 3 c OCH 3
1 a 2 b
Stereochemistry, CH PPh 2
2
Conformation, O CH 3 CH 3
and Stereoselectivity P P
O
CH PPh 2 Ph P PPh 2
2
2
CH O
3
DIOP Chiraphos
DIPAMP
4 d R R 5 d
P P R
R
P P
R R
BPE R R DuPHOS
a. H. B. Kagan and T.-P. Dang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 94, 6429 (1972).
b. M. D. Fryzuk and B. Bosnich, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 100, 5491 (1978).
c. W. S. Knowles, Acc. Chem. Res., 16, 106 (1983).
d. M. J. Burk, J. E. Feaster, W. A. Nugent, and R. L. Harlow, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 10125 (1993).
An especially important case is the enantioselective hydrogenation of -
amidoacrylic acids, which leads to -aminoacids. 136 A particularly detailed study was
carried out on the mechanism of reduction of methyl Z- -acetamidocinnamate by a
rhodium catalyst with the chiral diphosphine ligand DIPAMP. 137 It was concluded that
the reactant can bind reversibly to the catalyst to give either of two complexes. Addition
of hydrogen at rhodium then leads to a reactive rhodium hydride intermediate and
eventually to product. Interestingly, the addition of hydrogen occurs most rapidly in the
minor isomeric complex and the enantioselectivity is due to this kinetic preference. The
major isomer evidently encounters greater steric repulsions if hydrogenation proceeds
and is therefore less reactive. 138
CO CH 3
2
PhCH=C
NHCOCH
H 2 + 3 H 2
slower faster
major minor
complex Rh(DIPAMP) complex complex
Rh(DIPAMP)-hydride Rh(DIPAMP)-hydride
complex
complex
minor (R ) major (S )
product product
136
J. M. Brown, Chem. Soc. Rev., 22, 25 (1993). A. Pfaltz and J. M. Brown in Stereoselective Synthesis,
G. Helmchen, R. W. Hoffmann, J. Mulzer and E. Schauman, eds., Thieme, New York, 1996, Part D,
Sec. 2.5.1.2; U. Nagel and J. Albrecht, Top. Cataly., 5, 3 (1998).
137 C. R. Landis and J. Halpern, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 109, 1746 (1987).
138
S. Feldgus and C. R. Landis, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122, 12714 (2000).