Page 207 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 207
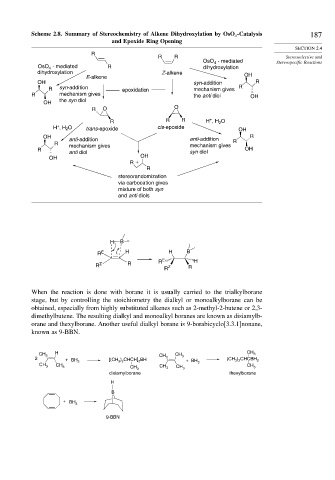
Scheme 2.8. Summary of Stereochemistry of Alkene Dihydroxylation by OsO -Catalysis 187
4
and Epoxide Ring Opening
SECTION 2.4
R
R R Stereoselective and
OsO 4 - mediated Stereospecific Reactions
- mediated R
OsO 4 dihydroxylation
dihydroxylation Z-alkene
E-alkene OH
OH syn-addition R
R syn-addition epoxidation mechanism gives R
R mechanism gives the anti diol OH
the syn diol
OH
R O O
+
R R R H , H O
2
+
H , H 2 O trans-epoxide cis-epoxide OH
OH anti-addition anti-addition R
R R
mechanism gives mechanism gives
R OH
anti diol syn diol
OH OH
R +
R
stereorandomization
via carbocation gives
mixture of both syn
and anti diols
H B
R E H H B
R Z R R E Z R H
R
When the reaction is done with borane it is usually carried to the trialkylborane
stage, but by controlling the stoichiometry the dialkyl or monoalkylborane can be
obtained, especially from highly substituted alkenes such as 2-methyl-2-butene or 2,3-
dimethylbutene. The resulting dialkyl and monoalkyl boranes are known as disiamylb-
orane and thexylborane. Another useful dialkyl borane is 9-borabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane,
known as 9-BBN.
CH H CH CH 3
2 3 + BH 3 [(CH ) CHCH] BH CH 3 3 + BH (CH 3 ) 2 CHCBH 2
CH 3 2 2 3 CH
3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 3
disiamylborane thexylborane
H
B
+
BH 3
9-BBN