Page 203 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 203
Another familiar and important example is syn and anti addition to double bonds. 183
There are many examples of stereospecific reactions involving additions to carbon-
carbon double bonds. Addition can be anti or syn, depending on the mechanism. If the SECTION 2.4
mechanism specifies syn or anti addition, different products will be obtained from the Stereoselective and
Stereospecific Reactions
E- and Z-isomers.
R 1 syn Y R 1 anti Y
R 2 R 1 R 2 R 2 R 1 R 2
X Y X Y
R 1 R 2 syn 1 R 1 R 2 anti 1
R 2 R 2
R R
X X
The examples in Scheme 2.7 include bromination, epoxidation and dihydroxylation,
and hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes.
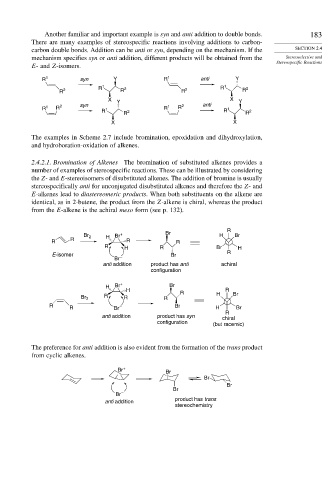
2.4.2.1. Bromination of Alkenes The bromination of substituted alkenes provides a
number of examples of stereospecific reactions. These can be illustrated by considering
the Z- and E-stereoisomers of disubstituted alkenes. The addition of bromine is usually
stereospecifically anti for unconjugated disubstituted alkenes and therefore the Z- and
E-alkenes lead to diastereomeric products. When both substituents on the alkene are
identical, as in 2-butene, the product from the Z-alkene is chiral, whereas the product
from the E-alkene is the achiral meso form (see p. 132).
R
Br
Br 2 H Br + H Br
R
R R R
R H R Br H
E-isomer Br R
–
Br
anti addition product has anti achiral
configuration
H Br + Br
H R R
R H Br
Br 2 R R
R R – Br H Br
Br
R
anti addition product has syn chiral
configuration (but racemic)
The preference for anti addition is also evident from the formation of the trans product
from cyclic alkenes.
Br + Br
Br
Br
Br
–
Br
product has trans
anti addition
stereochemistry