Page 594 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 594
575
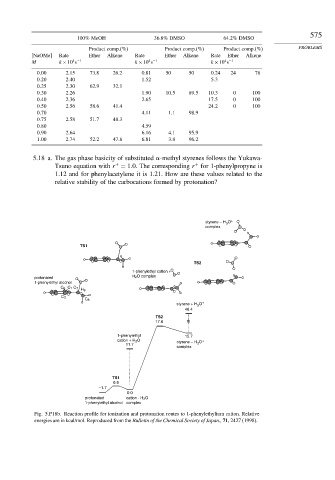
100% MeOH 36.8% DMSO 64.2% DMSO
Product comp.(%) Product comp.(%) Product comp.(%) PROBLEMS
NaOMe Rate Ether Alkene Rate Ether Alkene Rate Ether Alkene
4 −1
4 −1
4 −1
M k×10 s k×10 s k×10 s
0 00 2.15 73.8 26.2 0.81 50 50 0 24 24 76
0 20 2.40 1.52 5 3
0 25 2.30 62.9 32.1
0 30 2.26 1.90 10 5 89 5 10 3 0 100
0 40 2.36 2.65 17 5 0 100
0 50 2.56 58.6 41.4 24 2 0 100
0 70 4.11 1 1 98 9
0 75 2.58 51.7 48.3
0 80 4.59
0 90 2.64 6.16 4 1 95 9
1 00 2.74 52.2 47.8 6.81 3 8 96 2
5.18 a. The gas phase basicity of substituted -methyl styrenes follows the Yukawa-
Tsuno equation with r = 1 0. The corresponding r for 1-phenylpropyne is
+
+
1.12 and for phenylacetylene it is 1.21. How are these values related to the
relative stability of the carbocations formed by protonation?
styrene – H O +
3
complex
TS1
TS2
1-phenylethyl cation +
protonated H 2 O complex
1-phenylethyl alcohol
C 6 C 1 C 7
H 9
C 2
C 8
styrene + H O +
3
46.4
TS2
17.6
1-phenylethyl 15.7
cation + H 2 O styrene – H O +
11.7 3
complex
TS1
0.9
–1.7
0.0
protonated cation - H 2 O
1-phenylethyl alcohol complex
Fig. 5.P18b. Reaction profile for ionization and protonation routes to 1-phenylethylium cation. Relative
energies are in kcal/mol. Reproduced from the Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan., 71, 2427 (1998).