Page 1118 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1118
1094
CHAPTER 12 6 5
Oxidations 7 1.849 1.837 2.866 1.865 1.706 1.708 1.861
1.996 1.834 2.278
1.797 4
8 1.982 2.140 2.288
2.034 2.124 2.038 2.100 2.029
2.170 2.106
2 3
1
syn, endo syn, endo syn, exo syn, exo
∗
ΔG (rel)+2.09 + .91 –0.55 0.00
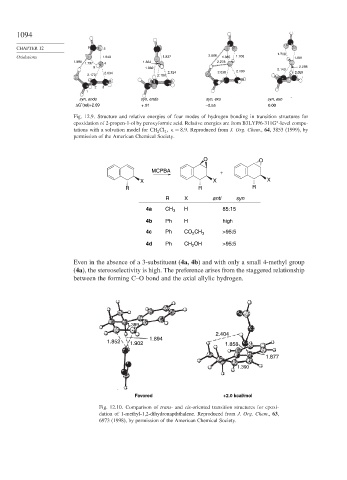
Fig. 12.9. Structure and relative energies of four modes of hydrogen bonding in transition structures for
epoxidation of 2-propen-1-ol by peroxyformic acid. Relative energies are from B3LYP/6-311G -level compu-
∗
tations with a solvation model for CH 2 Cl
= 8 9. Reproduced from J. Org. Chem., 64, 3853 (1999), by
2
permission of the American Chemical Society.
O O
MCPBA +
X X X
R R R
R X anti syn
4a CH 3 H 85:15
4b Ph H high
4c Ph CO 2 CH 3 >95:5
4d Ph CH 2 OH >95:5
Even in the absence of a 3-substituent (4a, 4b) and with only a small 4-methyl group
(4a), the stereoselectivity is high. The preference arises from the staggered relationship
between the forming C–O bond and the axial allylic hydrogen.
1.389
2.404
1.894
1.852 1.902 1.858
1.877
1.390
Favored +2.0 kcal/mol
Fig. 12.10. Comparison of trans- and cis-oriented transition structures for epoxi-
dation of 1-methyl-1,2-dihydronapththalene. Reproduced from J. Org. Chem., 63,
6973 (1998), by permission of the American Chemical Society.