Page 1123 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 1123
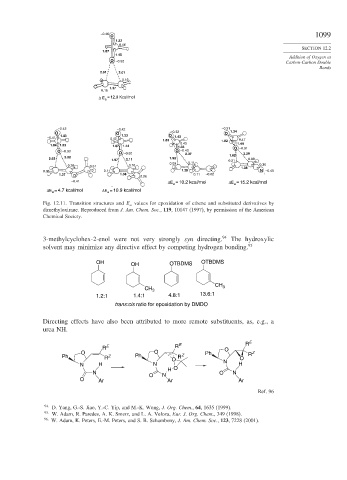
–0.46 1099
O
1.32
0.46
SECTION 12.2
1.87
1.45
Addition of Oxygen at
O –0.32
Carbon-Carbon Double
Bonds
2.01 2.01
0.16
1.37
0.16
= 12.9 Kcal/mol
Δ E a
–0.42 –0.42 –0.31
O O –0.32 O 1.34
1.43 1.33 O 1.43
–0.41 0.42 1.83 1.82 0.47
0.43 1.44
1.84 1.33 1.87 1.44 1.33 O –0.31
O –0.33 O –0.32 O –0.40 2.29
2.37
2.22 1.82
2.03 1.97 2.11 1.92 0.21 0.08
0.09 0.11
0.39 0.31 0.16 1.38 0.36
0.06 0.11 1.38 N –0.45
1.37 O 1.38 0.06 0.11 –0.02
–0.41 ΔE = 10.2 kcal/mol ΔE = 15.2 kcal/mol
a a
ΔE = 4.7 kcal/mol ΔE = 10.9 kcal/mol
a a
Fig. 12.11. Transition structures and E a values for epoxidation of ethene and substituted derivatives by
dimethyloxirane. Reproduced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 10147 (1997), by permission of the American
Chemical Society.
3-methylcyclohex-2-enol were not very strongly syn directing. 94 The hydroxylic
solvent may minimize any directive effect by competing hydrogen bonding. 95
OH OH OTBDMS OTBDMS
CH 3
CH 3
1.2:1 1.4:1 4.8:1 13.6:1
trans:cis ratio for epoxidation by DMDO
Directing effects have also been attributed to more remote substituents, as, e.g., a
urea NH.
R E R E O R E
O O Ph R Z
Ph R Z Ph O R Z O
N H N N H
H O
N O N O N
O Ar Ar Ar
Ref. 96
94 D. Yang, G.-S. Jiao, Y.-C. Yip, and M.-K. Wong, J. Org. Chem., 64, 1635 (1999).
95 W. Adam, R. Paredes, A. K. Smerz, and L. A. Veloza, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 349 (1998).
96
W. Adam, K. Peters, E.-M. Peters, and S. B. Schambony, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123, 7228 (2001).