Page 161 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 161
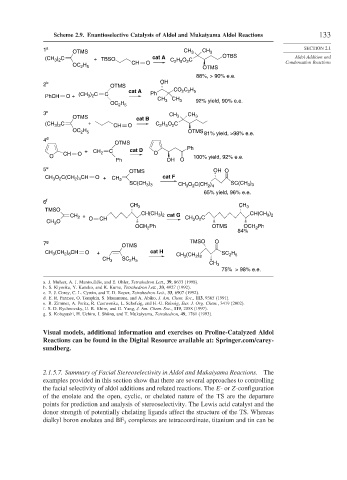
Scheme 2.9. Enantioselective Catalysis of Aldol and Mukaiyama Aldol Reactions 133
1 a OTMS CH 3 CH 3 SECTION 2.1
(CH ) C + TBSO cat A C H O C OTBS Aldol Addition and
3 2
2 5
2
H CH O Condensation Reactions
OTMS
OC 2 5
88%, > 90% e.e.
2 b OTMS OH
cat A Ph CO C H
2 2 5
PhCH O + (CH ) C C
3 2
CH CH
OC H 3 3 92% yield, 90% e.e.
2 5
3 c CH
OTMS cat B CH 3 3
(CH ) C + CH O C H O C
2 5
2
3 2
H
OC 2 5 OTMS 81% yield, >98% e.e.
4 d
OTMS
+ CH C cat D Ph
CH O 2 O
O 100% yield, 92% e.e.
Ph OH O
5 e OTMS OH O
O C(CH ) CH O cat F
CH 3 2 2 4 + CH 2
)
)
SC(CH 3 3 CH O C(CH ) SC(CH 3 3
3
2
2 4
65% yield, 96% e.e.
6 f
CH 3 CH 3
TMSO
)
3 2
CH 2 + O CH CH(CH 3 2 cat G CH O C CH(CH )
CH 3 O 3 2
OCH Ph OTMS OCH Ph
2
2
84%
7 g OTMS TMSO O
CH (CH ) CH O + cat H CH (CH ) SC H
3
2 8
2 5
CH 3 SC H 3 2 8
2 5
CH 3
75% > 98% e.e.
a. J. Mulzer, A. J. Mantoulidis, and E. Ohler, Tetrahedron Lett., 39, 8633 (1998).
b. S. Kiyooka, Y. Kaneko, and K. Kume, Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 4927 (1992).
c. E. J. Corey, C. L. Cywin, and T. D. Roper, Tetrahedron Lett., 33, 6907 (1992).
d. E. R. Parmee, O. Tempkin, S. Masamune, and A. Abiko, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 9365 (1991).
e. R. Zimmer, A. Peritz, R. Czerwonka, L. Schefzig, and H.-U. Reissig, Eur. J. Org. Chem., 3419 (2002).
f. S. D. Rychnovsky, U. R. Khire, and G. Yang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 2058 (1997).
g. S. Kobayashi, H. Uchiro, I. Shiina, and T. Mukaiyama, Tetrahedron, 49, 1761 (1993).
Visual models, additional information and exercises on Proline-Catalyzed Aldol
Reactions can be found in the Digital Resource available at: Springer.com/carey-
sundberg.
2.1.5.7. Summary of Facial Stereoselectivity in Aldol and Mukaiyama Reactions. The
examples provided in this section show that there are several approaches to controlling
the facial selectivity of aldol additions and related reactions. The E-or Z-configuration
of the enolate and the open, cyclic, or chelated nature of the TS are the departure
points for prediction and analysis of stereoselectivity. The Lewis acid catalyst and the
donor strength of potentially chelating ligands affect the structure of the TS. Whereas
dialkyl boron enolates and BF complexes are tetracoordinate, titanium and tin can be
3