Page 183 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 183
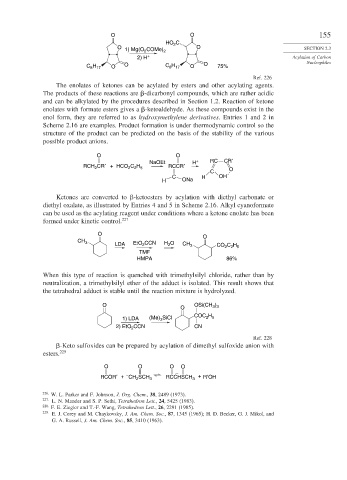
O O 155
HO C
2
O O SECTION 2.3
1) Mg(O 2 COMe) 2
2) H + Acylation of Carbon
C H O O C H O O 75% Nucleophiles
8 17
8 17
Ref. 226
The enolates of ketones can be acylated by esters and other acylating agents.
The products of these reactions are -dicarbonyl compounds, which are rather acidic
and can be alkylated by the procedures described in Section 1.2. Reaction of ketone
enolates with formate esters gives a -ketoaldehyde. As these compounds exist in the
enol form, they are referred to as hydroxymethylene derivatives. Entries 1 and 2 in
Scheme 2.16 are examples. Product formation is under thermodynamic control so the
structure of the product can be predicted on the basis of the stability of the various
possible product anions.
O O
NaOEt H + RC CR′
2 2 5
RCH 2 CR′ + HCO C H RCCR′ O
C
C H OH
H ONa
Ketones are converted to -ketoesters by acylation with diethyl carbonate or
diethyl oxalate, as illustrated by Entries 4 and 5 in Scheme 2.16. Alkyl cyanoformate
can be used as the acylating reagent under conditions where a ketone enolate has been
formed under kinetic control. 227
O
O
CH 3 EtO CCN H O
LDA 2 2 CH 3 CO C H
2 2 5
TMF
HMPA 86%
When this type of reaction is quenched with trimethylsilyl chloride, rather than by
neutralization, a trimethylsilyl ether of the adduct is isolated. This result shows that
the tetrahedral adduct is stable until the reaction mixture is hydrolyzed.
)
O OSi(CH 3 3
O
2 5
1) LDA (Me) SiCl COC H
3
CCN CN
2) EtO 2
Ref. 228
-Keto sulfoxides can be prepared by acylation of dimethyl sulfoxide anion with
esters. 229
O O O O
–
RCOR′ + – CH SCH 3 RCCHSCH 3 + R′OH
2
226 W. L. Parker and F. Johnson, J. Org. Chem., 38, 2489 (1973).
227
L. N. Mander and S. P. Sethi, Tetrahedron Lett., 24, 5425 (1983).
228 F. E. Ziegler and T.-F. Wang, Tetrahedron Lett., 26, 2291 (1985).
229
E. J. Corey and M. Chaykovsky, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 87, 1345 (1965); H. D. Becker, G. J. Mikol, and
G. A. Russell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 85, 3410 (1963).