Page 184 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 184
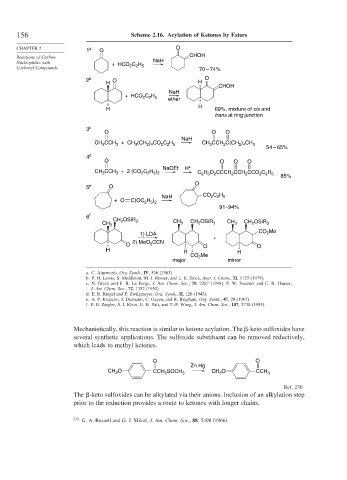
156 Scheme 2.16. Acylation of Ketones by Esters
CHAPTER 2 1 a O O
Reactions of Carbon CHOH
Nucleophiles with + HCO C H NaH
Carbonyl Compounds 2 2 5 70 – 74%
2 b O H O
H
CHOH
NaH
+ HCO C H ether
2 2 5
H
H 69%, mixture of cis and
trans at ring junction
3 c
O O O
NaH
CH CCH + CH (CH ) CO C H CH CCH C(CH ) CH 3
3
2 2 5
2
2 4
3
3
2 4
3
54 – 65%
4 d
O O O O
NaOEt H +
CH CCH + 2 (CO C H ) C 2 H 5 O 2 CCCH 2 CCH 2 CCO 2 C 2 H 5
3
2 2 5 2
3
85%
O
5 e O
C H
NaH CO 2 2 5
+ O C(OC H )
2 5 2
91–94%
6 f
CH OSiR 3 CH CH OSiR
2
CH 3 3 2 3 CH 3 CH 2 OSiR 3
CO Me
1) LDA 2
+
2) MeO CCN
O 2 O O
H H H
CO 2 Me
major minor
a. C. Ainsworth, Org. Synth., IV, 536 (1963).
b. P. H. Lewis, S. Middleton, M. J. Rosser, and L. E. Stock, Aust. J. Chem., 32, 1123 (1979).
c. N. Green and F. B. La Forge, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 70, 2287 (1948); F. W. Swamer and C. R. Hauser,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 72, 1352 (1950).
d. E. R. Riegel and F. Zwilgmeyer, Org. Synth., II, 126 (1943).
e. A. P. Krapcho, J. Diamanti, C. Cayen, and R. Bingham, Org. Synth., 47, 20 (1967).
f. F. E. Ziegler, S. I. Klein, U. K. Pati, and T.-F. Wang, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 107, 2730 (1985).
Mechanistically, this reaction is similar to ketone acylation. The -keto sulfoxides have
several synthetic applications. The sulfoxide substituent can be removed reductively,
which leads to methyl ketones.
O O
Zn Hg
CH O CCH 2 SOCH 3 CH 3 O CCH 3
3
Ref. 230
The -keto sulfoxides can be alkylated via their anions. Inclusion of an alkylation step
prior to the reduction provides a route to ketones with longer chains.
230
G. A. Russell and G. J. Mikol, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 88, 5498 (1966).