Page 310 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 310
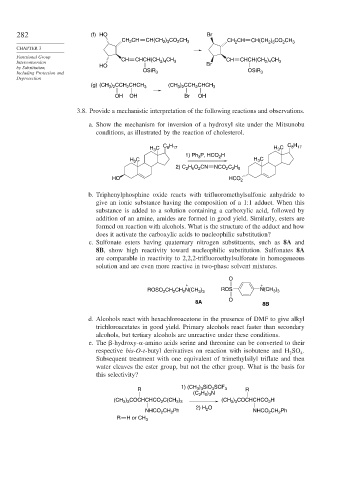
282 (f) HO Br
CH CH CH(CH ) CO CH 3 CH CH CH(CH ) CO CH 3
2
2 3
2
2
2 3
2
CHAPTER 3
Functional Group CH CHCH(CH ) CH CH ) CH
Interconversion 2 4 3 Br CHCH(CH 2 4 3
by Substitution, HO OSiR OSiR
Including Protection and 3 3
Deprotection
(g) (CH 3 ) 2 CCH 2 CHCH 3 (CH 3 ) 2 CCH 2 CHCH 3
OH OH Br OH
3.8. Provide a mechanistic interpretation of the following reactions and observations.
a. Show the mechanism for inversion of a hydroxyl site under the Mitsunobu
conditions, as illustrated by the reaction of cholesterol.
H C H
H C C 8 17 H C 8 17
3
3
1) Ph P, HCO H
3
2
H C H C
3
3
2) C H O CN NCO C H
2
2 5
2 2 5
HO HCO 2
b. Triphenylphosphine oxide reacts with trifluoromethylsulfonic anhydride to
give an ionic substance having the composition of a 1:1 adduct. When this
substance is added to a solution containing a carboxylic acid, followed by
addition of an amine, amides are formed in good yield. Similarly, esters are
formed on reaction with alcohols. What is the structure of the adduct and how
does it activate the carboxylic acids to nucleophilic substitution?
c. Sulfonate esters having quaternary nitrogen substituents, such as 8A and
8B, show high reactivity toward nucleophilic substitution. Sulfonates 8A
are comparable in reactivity to 2,2,2-trifluoroethylsulfonate in homogeneous
solution and are even more reactive in two-phase solvent mixtures.
O
+ +
ROSO CH CH N(CH ) ROS N(CH )
3 3
2
3 3
2
2
O
8A 8B
d. Alcohols react with hexachloroacetone in the presence of DMF to give alkyl
trichloroacetates in good yield. Primary alcohols react faster than secondary
alcohols, but tertiary alcohols are unreactive under these conditions.
e. The -hydroxy- -amino acids serine and threonine can be converted to their
respective bis-O-t-butyl derivatives on reaction with isobutene and H SO .
2 4
Subsequent treatment with one equivalent of trimethylsilyl triflate and then
water cleaves the ester group, but not the ether group. What is the basis for
this selectivity?
1) (CH ) SiO SCF
R 3 3 3 3 R
(C H ) N
2 5 3
(CH ) COCHCHCO C(CH ) (CH ) COCHCHCO H
2
3 3
2
3 3
3 3
O
NHCO CH Ph 2) H 2 NHCO CH Ph
2
2
2
2
R H or CH 3