Page 419 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 419
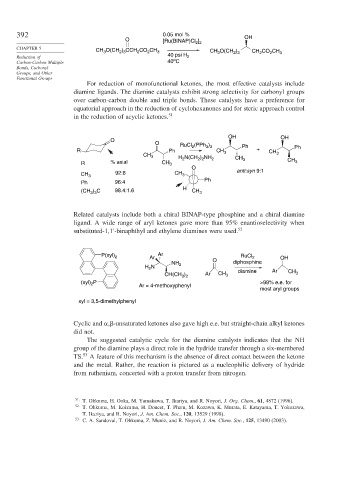
392 0.05 mol %
O ] OH
[Ru(BINAP)Cl 2 2
CHAPTER 5 CH O(CH ) CCH CO CH 3 CH O(CH ) CH CO CH
2
2
3
2 3
Reduction of 40 psi H 2 3 2 3 2 2 3
o
Carbon-Carbon Multiple 40 C
Bonds, Carbonyl
Groups, and Other
Functional Groups
For reduction of monofunctional ketones, the most effective catalysts include
diamine ligands. The diamine catalysts exhibit strong selectivity for carbonyl groups
over carbon-carbon double and triple bonds. These catalysts have a preference for
equatorial approach in the reduction of cyclohexanones and for steric approach control
in the reduction of acyclic ketones. 51
OH OH
O
O RuCl (PPh ) Ph
R Ph 2 3 3 CH 3 + CH Ph
CH 3 H N(CH ) NH 2 CH 3
2 2
2
R % axial CH 3 3 CH 3
O
CH 3 92:8 CH 3 anti:syn 9:1
Ph
Ph 96:4
H
(CH ) C 98.4:1.6 CH 3
3 3
Related catalysts include both a chiral BINAP-type phosphine and a chiral diamine
ligand. A wide range of aryl ketones gave more than 95% enantioselectivity when
substituted-1,1 -binaphthyl and ethylene diamines were used. 52
P(xyl) 2 Ar Ar RuCl 2 OH
NH 2 O diphosphine
H 2 N
diamine Ar CH
CH(CH ) Ar CH 3 3
3 2
(xyl) P Ar = 4-methoxyphenyl >99% e.e. for
2
most aryl groups
xyl = 3,5-dimethylphenyl
Cyclic and , -unsaturated ketones also gave high e.e. but straight-chain alkyl ketones
did not.
The suggested catalytic cycle for the diamine catalysts indicates that the NH
group of the diamine plays a direct role in the hydride transfer through a six-membered
53
TS. A feature of this mechanism is the absence of direct contact between the ketone
and the metal. Rather, the reaction is pictured as a nucleophilic delivery of hydride
from ruthenium, concerted with a proton transfer from nitrogen.
51 T. Ohkuma, H. Ooka, M. Yamakawa, T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, J. Org. Chem., 61, 4872 (1996).
52 T. Ohkuma, M. Koizuma, H. Doucet, T. Pham, M. Kozawa, K. Murata, E. Katayama, T. Yokozawa,
T. Ikariya, and R. Noyori, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 120, 13529 (1998).
53
C. A. Sandoval, T. Ohkuma, Z. Muniz, and R. Noyori, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 13490 (2003).