Page 414 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 414
the addition of two hydrogens to the alkene-catalyst complex, followed by formation 387
of an alkyliridium intermediate and reductive elimination.
SECTION 5.1
Addition of Hydrogen at
S R Carbon-Carbon Multiple
CH L L Bonds
RCH 2 3 Ir
S H
H
S
H S solvent L Ir H L
L Ir L L ligand H
H R
H H H
R H L Ir L H 2
H
H
R
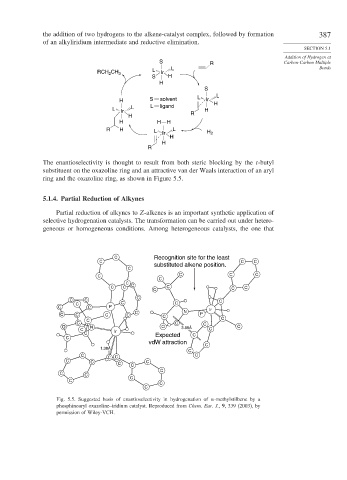
The enantioselectivity is thought to result from both steric blocking by the t-butyl
substituent on the oxazoline ring and an attractive van der Waals interaction of an aryl
ring and the oxazoline ring, as shown in Figure 5.5.
5.1.4. Partial Reduction of Alkynes
Partial reduction of alkynes to Z-alkenes is an important synthetic application of
selective hydrogenation catalysts. The transformation can be carried out under hetero-
geneous or homogeneous conditions. Among heterogeneous catalysts, the one that
C Recognition site for the least
C C C
substituted alkene position.
C
C C C
C
C
C
C C C C C C
C
C
C C C
C C C
C C P lr
C N
C C C C C P
C C
C C C
O N O 3.89Å C
C lr C
C C
C Expected
vdW attraction
C
1.38Å
C
C C
C C
C C C
C
C
C
C
C
C C
C
C
Fig. 5.5. Suggested basis of enantioselectivity in hydrogenation of -methylstilbene by a
phosphinoaryl oxazoline–iridium catalyst. Reproduced from Chem. Eur. J., 9, 339 (2003), by
permission of Wiley-VCH.