Page 754 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 754
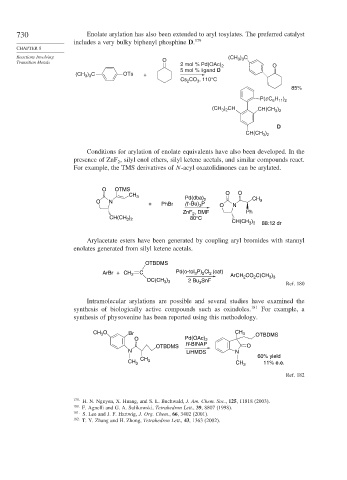
730 Enolate arylation has also been extended to aryl tosylates. The preferred catalyst
includes a very bulky biphenyl phosphine D. 179
CHAPTER 8
) C
Reactions Involving (CH 3 3
Transition Metals O 2 mol % Pd(OAc) 2 O
5 mol % ligand D
(CH ) C OTs +
3 3
Cs CO , 110°C
3
2
85%
P(c C H )
6 11 2
(CH ) CH CH(CH )
3 2
3 2
D
CH(CH )
3 2
Conditions for arylation of enolate equivalents have also been developed. In the
presence of ZnF , silyl enol ethers, silyl ketene acetals, and similar compounds react.
2
For example, the TMS derivatives of N-acyl oxazolidinones can be arylated.
O OTMS
CH 3 Pd(dba) O O
O N + PhBr (t -Bu) P 2 O N CH 3
3
ZnF 2 , DMF Ph
)
CH(CH 3 2 80°C
)
CH(CH 3 2 88:12 dr
Arylacetate esters have been generated by coupling aryl bromides with stannyl
enolates generated from silyl ketene acetals.
OTBDMS
C Pd(o-tol P) Cl (cat)
ArBr +CH 2 3 2 2
ArCH CO C(CH )
3 3
2
2
)
OC(CH 3 3 2 Bu 3 SnF
Ref. 180
Intramolecular arylations are possible and several studies have examined the
synthesis of biologically active compounds such as oxindoles. 181 For example, a
synthesis of physovenine has been reported using this methodology.
CH 3 O Br CH 3 OTBDMS
O Pd(OAc) 2
OTBDMS R-BINAP O
N LiHMDS N
60% yield
CH 3 CH 3 CH 3 11% e.e.
Ref. 182
179
H. N. Nguyen, X. Huang, and S. L. Buchwald, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 125, 11818 (2003).
180
F. Agnelli and G. A. Sulikowski, Tetrahedron Lett., 39, 8807 (1998).
181 S. Lee and J. F. Hartwig, J. Org. Chem., 66, 3402 (2001).
182
T. Y. Zhang and H. Zhong, Tetrahedron Lett., 43, 1363 (2002).