Page 835 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 835
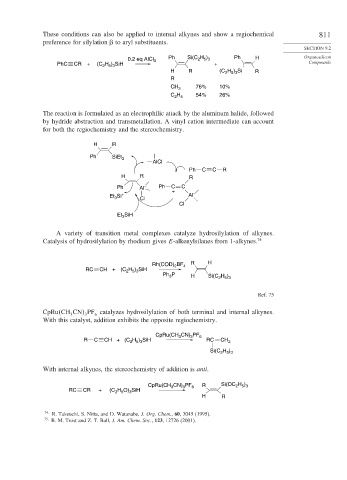
These conditions can also be applied to internal alkynes and show a regiochemical 811
preference for silylation to aryl substituents.
SECTION 9.2
0.2 eq AlCl 3 Ph Si(C H ) Ph H Organosilicon
2 5 3
PhC CR + (C H ) SiH + Compounds
2 5 3
H R (C H ) Si R
2 5 3
R
CH 3 76% 10%
C H 54% 26%
2 5
The reaction is formulated as an electrophilic attack by the aluminum halide, followed
by hydride abstraction and transmetallation. A vinyl cation intermediate can account
for both the regiochemistry and the stereochemistry.
H R
Ph SiEt 3
AlCl
Ph C C R
H R R
Ph Al – Ph C C
+ –
Et Si + Cl Al
3
Cl
Et 3 SiH
A variety of transition metal complexes catalyze hydrosilylation of alkynes.
Catalysis of hydrosilylation by rhodium gives E-alkenylsilanes from 1-alkynes. 74
Rh(COD) BF 4 R H
2
RC CH +(C H ) SiH
2 5 3
Ph P H Si(C 2 5 3
H )
3
Ref. 75
CpRu CH CN PF catalyzes hydrosilylation of both terminal and internal alkynes.
3
6
3
With this catalyst, addition exhibits the opposite regiochemistry.
CpRu(CH CN) PF 6
3
3
R C CH + (C H ) SiH RC CH 2
2 5 3
Si(C H )
2 5 3
With internal alkynes, the stereochemistry of addition is anti.
CpRu(CH CN) PF 6 R Si(OC H )
2 5 3
3
3
RC CR + (C H O) SiH
3
2 5
H R
74 R. Takeuchi, S. Nitta, and D. Watanabe, J. Org. Chem., 60, 3045 (1995).
75
B. M. Trost and Z. T. Ball, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 123, 12726 (2001).