Page 908 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 908
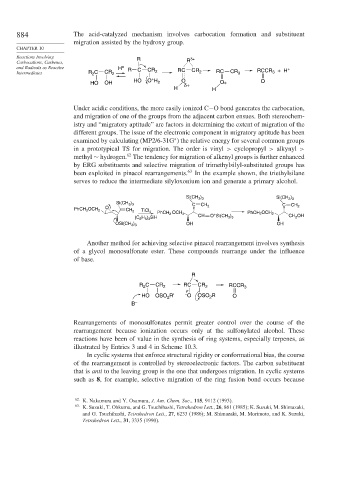
884 The acid-catalyzed mechanism involves carbocation formation and substituent
migration assisted by the hydroxy group.
CHAPTER 10
Reactions Involving R δ+
Carbocations, Carbenes, R
and Radicals as Reactive H + R C RC CR +
Intermediates R C CR 2 CR 2 2 RC CR 3 RCCR 3 + H
2
+
HO OH HO O H 2 O δ+ O+ O
H H
Under acidic conditions, the more easily ionized C−O bond generates the carbocation,
and migration of one of the groups from the adjacent carbon ensues. Both stereochem-
istry and “migratory aptitude” are factors in determining the extent of migration of the
different groups. The issue of the electronic component in migratory aptitude has been
examined by calculating (MP2/6-31G ) the relative energy for several common groups
∗
in a prototypical TS for migration. The order is vinyl > cyclopropyl > alkynyl >
62
methyl ∼ hydrogen. The tendency for migration of alkenyl groups is further enhanced
by ERG substituents and selective migration of trimethylsilyl-substituted groups has
been exploited in pinacol rearrangements. 63 In the example shown, the triethylsilane
serves to reduce the intermediate silyloxonium ion and generate a primary alcohol.
Si(CH 3 ) 3 Si(CH 3 ) 3
Si(CH 3 ) 3 C C
O CH 2 CH 2
PhCH 2 OCH 2 CH 2 TiCl 4
PhCH 2 OCH 2 + PhCH 2 OCH 2
(C 2 H 5 ) 3 SiH CH O Si(CH 3 ) 3 CH 2 OH
OH OH
OSi(CH 3 ) 3
Another method for achieving selective pinacol rearrangement involves synthesis
of a glycol monosulfonate ester. These compounds rearrange under the influence
of base.
R
C CR RC CR RCCR
R 2 2 2 3
HO OSO R' – O OSO R O
2
2
B –
Rearrangements of monosulfonates permit greater control over the course of the
rearrangement because ionization occurs only at the sulfonylated alcohol. These
reactions have been of value in the synthesis of ring systems, especially terpenes, as
illustrated by Entries 3 and 4 in Scheme 10.3.
In cyclic systems that enforce structural rigidity or conformational bias, the course
of the rearrangement is controlled by stereoelectronic factors. The carbon substituent
that is anti to the leaving group is the one that undergoes migration. In cyclic systems
such as 8, for example, selective migration of the ring fusion bond occurs because
62 K. Nakamura and Y. Osamura, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 9112 (1993).
63
K. Suzuki, T. Ohkuma, and G. Tsuchihashi, Tetrahedron Lett., 26, 861 (1985); K. Suzuki, M. Shimazaki,
and G. Tsuchihashi, Tetrahedron Lett., 27, 6233 (1986); M. Shimazaki, M. Morimoto, and K. Suzuki,
Tetrahedron Lett., 31, 3335 (1990).