Page 968 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 968
944
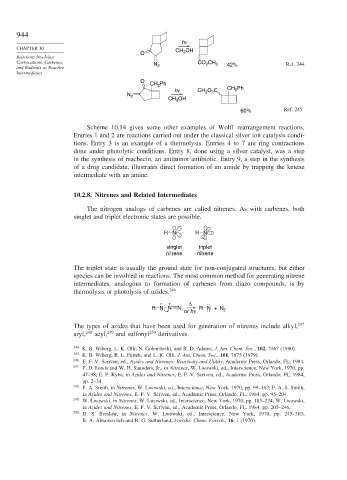
h ν
CHAPTER 10 CH OH
O 3
Reactions Involving
Carbocations, Carbenes, CO CH
N 2 2 3 42% Ref. 244
and Radicals as Reactive
Intermediates
O
CH Ph
2
hν CH O C CH Ph
2
N 2 3 2
CH 3 OH
60% Ref. 245
Scheme 10.14 gives some other examples of Wolff rearrangement reactions.
Entries 1 and 2 are reactions carried out under the classical silver ion catalysis condi-
tions. Entry 3 is an example of a thermolysis. Entries 4 to 7 are ring contractions
done under photolytic conditions. Entry 8, done using a silver catalyst, was a step
in the synthesis of macbecin, an antitumor antibiotic. Entry 9, a step in the synthesis
of a drug candidate, illustrates direct formation of an amide by trapping the ketene
intermediate with an amine.
10.2.8. Nitrenes and Related Intermediates
The nitrogen analogs of carbenes are called nitrenes. As with carbenes, both
singlet and triplet electronic states are possible.
R N R N
. .
singlet triplet
nitrene nitrene
The triplet state is usually the ground state for non-conjugated structures, but either
species can be involved in reactions. The most common method for generating nitrene
intermediates, analogous to formation of carbenes from diazo compounds, is by
thermolysis or photolysis of azides. 246
:– + Δ :
R N N R N + N
or h ν : 2
N :
The types of azides that have been used for generation of nitrenes include alkyl, 247
aryl, 248 acyl, 249 and sulfonyl 250 derivatives.
244 K. B. Wiberg, L. K. Olli, N. Golembeski, and R. D. Adams, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 102, 7467 (1980).
245
K. B. Wiberg, B. L. Furtek, and L. K. Olli, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 101, 7675 (1979).
246 E. F. V. Scriven, ed., Azides and Nitrenes: Reactivity and Utility, Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 1984.
247 F. D. Lewis and W. H. Saunders, Jr., in Nitrenes, W. Lwowski, ed., Interscience, New York, 1970, pp.
47–98; E. P. Kyba, in Azides and Nitrenes, E. F. V. Scriven, ed., Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 1984,
pp. 2–34.
248
P. A. Smith, in Nitrenes, W. Lwowski, ed., Interscience, New York, 1970, pp. 99–162; P. A. S. Smith,
in Azides and Nitrenes, E. F. V. Scriven, ed., Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 1984, pp. 95–204.
249 W. Lwowski, in Nitrenes, W. Lwowski, ed., Interscience, New York, 1970, pp. 185–224; W. Lwowski,
in Azides and Nitrenes, E. F. V. Scriven, ed., Academic Press, Orlando, FL, 1984, pp. 205–246.
250
D. S. Breslow, in Nitrenes, W. Lwowski, ed., Interscience, New York, 1970, pp. 245–303;
R. A. Abramovitch and R. G. Sutherland, Fortshr. Chem. Forsch., 16, 1 (1970).