Page 970 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 970
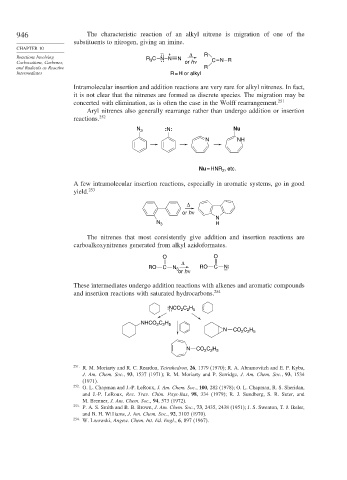
946 The characteristic reaction of an alkyl nitrene is migration of one of the
substituents to nitrogen, giving an imine.
CHAPTER 10
: – + Δ
Reactions Involving N N R
3
Carbocations, Carbenes, R CN : or h ν C N R
and Radicals as Reactive R
Intermediates R = H or alkyl
Intramolecular insertion and addition reactions are very rare for alkyl nitrenes. In fact,
it is not clear that the nitrenes are formed as discrete species. The migration may be
concerted with elimination, as is often the case in the Wolff rearrangement. 251
Aryl nitrenes also generally rearrange rather than undergo addition or insertion
reactions. 252
N 3 :N: Nu
N NH
Nu = HNR , etc.
2
A few intramolecular insertion reactions, especially in aromatic systems, go in good
yield. 253
Δ
or h ν
N
N 3 H
The nitrenes that most consistently give addition and insertion reactions are
carboalkoxynitrenes generated from alkyl azidoformates.
O O
Δ
RO C N 3 or h ν RO C N : :
These intermediates undergo addition reactions with alkenes and aromatic compounds
and insertion reactions with saturated hydrocarbons. 254
:NCO C H
2 2 5
:
NHCO C H
2 2 5
N CO C H
2 2 5
N CO C H
2 2 5
251
R. M. Moriarty and R. C. Reardon, Tetrahedron, 26, 1379 (1970); R. A. Abramovitch and E. P. Kyba,
J. Am. Chem. Soc., 93, 1537 (1971); R. M. Moriarty and P. Serridge, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 93, 1534
(1971).
252 O. L. Chapman and J.-P. LeRoux, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 100, 282 (1978); O. L. Chapman, R. S. Sheridan,
and J.-P. LeRoux, Rec. Trav. Chim. Pays-Bas, 98, 334 (1979); R. J. Sundberg, S. R. Suter, and
M. Brenner, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 94, 573 (1972).
253 P. A. S. Smith and B. B. Brown, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 73, 2435, 2438 (1951); J. S. Swenton, T. J. Ikeler,
and B. H. Williams, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 92, 3103 (1970).
254
W. Lwowski, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 6, 897 (1967).