Page 282 - Advanced Thermodynamics for Engineers, Second Edition
P. 282
12.9 THE EFFECT OF PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE 271
Table 12.1 Amount of Products for Constant Pressure Combustion of
Methane in Air Initial Temperature [ 1000 K; Equivalence Ratio [ 1.00
Pressure (bar) No Dissociation 1 10 100
Amount of CO 2 1 0.6823 0.7829 0.8665
Amount of CO 0 0.3170 0.2170 0.1335
Amount of H 2 O 2 1.8654 1.920 1.9558
0 0.1343 0.0801 0.0444
Amount of H 2
0 0.2258 0.1485 0.0889
Amount of O 2
7.52 7.52 7.52 7.52
Amount of N 2
Total amount of substance 10.52 10.7448 10.6685 10.6091
where a 1 is the degree of dissociation of the CO 2 reaction and a 2 is the degree of dissociation of the
H 2 O reaction. It can be seen that dissociation tends to increase the amount of substance of products,
and hence the effect of pressure should be to reduce the degree of dissociation. This effect can be seen
quite clearly in Table 12.1, where the amount of substance of products is compared under four sets of
conditions: no dissociation, dissociation at p ¼ 1 bar, dissociation at p ¼ 10 bar and dissociation at
p ¼ 100 bar. The minimum total amount of substance occurs when there is no dissociation, with the
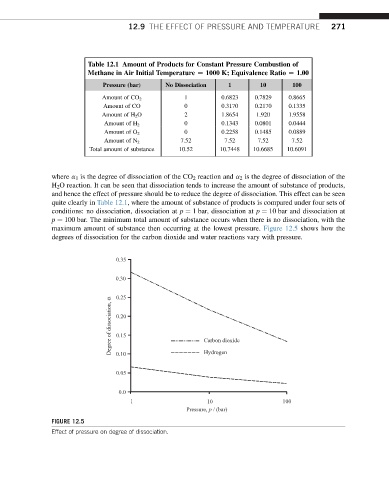
maximum amount of substance then occurring at the lowest pressure. Figure 12.5 shows how the
degrees of dissociation for the carbon dioxide and water reactions vary with pressure.
0.35
0.30
0.25
Degree of dissociation, α 0.20 Carbon dioxide
0.15
0.10
0.05 Hydrogen
0.0
1 10 100
Pressure, p / (bar)
FIGURE 12.5
Effect of pressure on degree of dissociation.