Page 340 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 340
15.4 FLAMES 329
(a) (b)
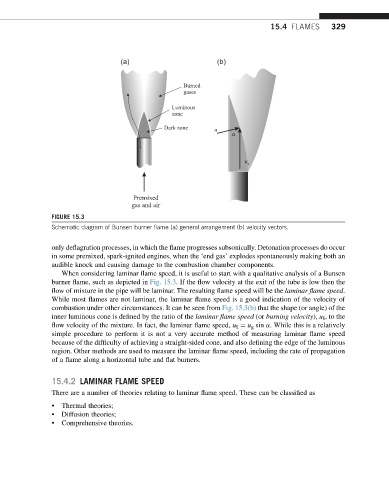
FIGURE 15.3
Schematic diagram of Bunsen burner flame (a) general arrangement (b) velocity vectors.
only deflagration processes, in which the flame progresses subsonically. Detonation processes do occur
in some premixed, spark-ignited engines, when the ‘end gas’ explodes spontaneously making both an
audible knock and causing damage to the combustion chamber components.
When considering laminar flame speed, it is useful to start with a qualitative analysis of a Bunsen
burner flame, such as depicted in Fig. 15.3. If the flow velocity at the exit of the tube is low then the
flow of mixture in the pipe will be laminar. The resulting flame speed will be the laminar flame speed.
While most flames are not laminar, the laminar flame speed is a good indication of the velocity of
combustion under other circumstances. It can be seen from Fig. 15.3(b) that the shape (or angle) of the
inner luminous cone is defined by the ratio of the laminar flame speed (or burning velocity), u [ , to the
flow velocity of the mixture. In fact, the laminar flame speed, u [ ¼ u g sin a. While this is a relatively
simple procedure to perform it is not a very accurate method of measuring laminar flame speed
because of the difficulty of achieving a straight-sided cone, and also defining the edge of the luminous
region. Other methods are used to measure the laminar flame speed, including the rate of propagation
of a flame along a horizontal tube and flat burners.
15.4.2 LAMINAR FLAME SPEED
There are a number of theories relating to laminar flame speed. These can be classified as
• Thermal theories;
• Diffusion theories;
• Comprehensive theories.