Page 436 - Advanced thermodynamics for engineers
P. 436
426 CHAPTER 18 LIQUEFACTION OF GASES
0
0
where b is the overall coefficient of the combined plant, and b 1 and b 2 are the coefficients of per-
0
formance of the separate parts of the cascade. The coefficient of performance of the overall plant is less
than that of either individual part.
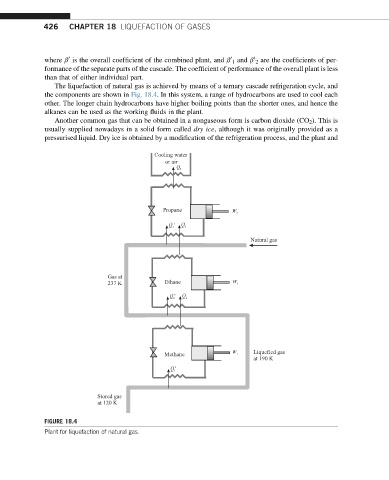
The liquefaction of natural gas is achieved by means of a ternary cascade refrigeration cycle, and
the components are shown in Fig. 18.4. In this system, a range of hydrocarbons are used to cool each
other. The longer chain hydrocarbons have higher boiling points than the shorter ones, and hence the
alkanes can be used as the working fluids in the plant.
Another common gas that can be obtained in a nongaseous form is carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). This is
usually supplied nowadays in a solid form called dry ice, although it was originally provided as a
pressurised liquid. Dry ice is obtained by a modification of the refrigeration process, and the plant and
Cooling water
or air
Q
Propane W
Q ' Q
Natural gas
Gas at
237 K Ethane W
Q ' Q
Methane W Liquefied gas
at 190 K
Q '
Stored gas
at 120 K
FIGURE 18.4
Plant for liquefaction of natural gas.