Page 285 - Advances in Biomechanics and Tissue Regeneration
P. 285
14.4 3D PRINTING OF PERSONALIZED SILICONE IMPLANT 283
Shear thinning
Yield stress
Thixotropy
(A)
Newtonian
shear thickening Shear thinning
Viscocity
Lower shear
High shear
stress risk stress
Shear rate
(B) (C)
High yield stress Low yield stress Adapted yield
stress
Shear rate
Yield stress Stress
(D) (E) Shear thinning and thoxtopic time are supposed adapted
High thixotropic Low thixotropic
time time
Storage modulus
Thixotropic Time
(F) time (G) Shear thinning and yield stress are supposed adapted
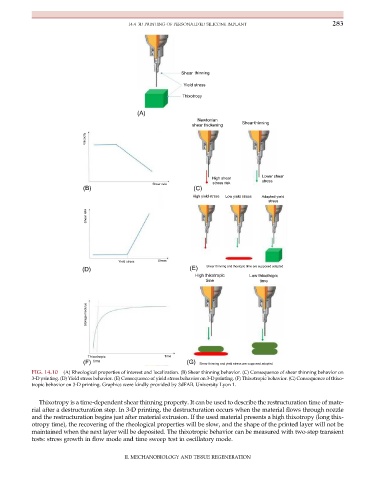
FIG. 14.10 (A) Rheological properties of interest and localization. (B) Shear thinning behavior. (C) Consequence of shear thinning behavior on
3-D printing. (D) Yield stress behavior. (E) Consequence of yield stress behavior on 3-D printing. (F) Thixotropic behavior. (G) Consequence of thixo-
tropic behavior on 3-D printing. Graphics were kindly provided by 3dFAB, University Lyon 1.
Thixotropy is a time-dependent shear thinning property. It can be used to describe the restructuration time of mate-
rial after a destructuration step. In 3-D printing, the destructuration occurs when the material flows through nozzle
and the restructuration begins just after material extrusion. If the used material presents a high thixotropy (long thix-
otropy time), the recovering of the rheological properties will be slow, and the shape of the printed layer will not be
maintained when the next layer will be deposited. The thixotropic behavior can be measured with two-step transient
tests: stress growth in flow mode and time sweep test in oscillatory mode.
II. MECHANOBIOLOGY AND TISSUE REGENERATION