Page 65 - Advances in Biomechanics and Tissue Regeneration
P. 65
REFERENCES 59
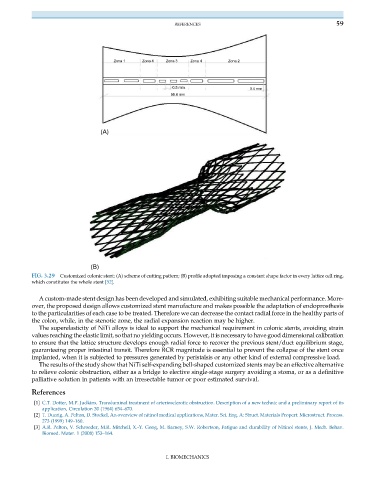
Zona 1 Zona 4 Zona 3 Zona 4 Zona 2
0.5 mm
0.4 mm
98.8 mm
(A)
(B)
FIG. 3.29 Customized colonic stent: (A) scheme of cutting pattern; (B) profile adopted imposing a constant shape factor in every lattice cell ring,
which constitutes the whole stent [52].
A custom-made stent design has been developed and simulated, exhibiting suitable mechanical performance. More-
over, the proposed design allows customized stent manufacture and makes possible the adaptation of endoprosthesis
to the particularities of each case to be treated. Therefore we can decrease the contact radial force in the healthy parts of
the colon, while, in the stenotic zone, the radial expansion reaction may be higher.
The superelasticity of NiTi alloys is ideal to support the mechanical requirement in colonic stents, avoiding strain
values reaching the elastic limit, so that no yielding occurs. However, it is necessary to have good dimensional calibration
to ensure that the lattice structure develops enough radial force to recover the previous stent/duct equilibrium stage,
guaranteeing proper intestinal transit. Therefore RCR magnitude is essential to prevent the collapse of the stent once
implanted, when it is subjected to pressures generated by peristalsis or any other kind of external compressive load.
The results of the study show that NiTi self-expanding bell-shaped customized stents may be an effective alternative
to relieve colonic obstruction, either as a bridge to elective single-stage surgery avoiding a stoma, or as a definitive
palliative solution in patients with an irresectable tumor or poor estimated survival.
References
[1] C.T. Dotter, M.P. Judkins, Transluminal treatment of arteriosclerotic obstruction. Description of a new technic and a preliminary report of its
application, Circulation 30 (1964) 654–670.
[2] T. Duerig, A. Pelton, D. Stockel, An overview of nitinol medical applications, Mater. Sci. Eng. A: Struct. Materials Propert. Microstruct. Process.
273 (1999) 149–160.
[3] A.R. Pelton, V. Schroeder, M.R. Mitchell, X.-Y. Gong, M. Barney, S.W. Robertson, Fatigue and durability of Nitinol stents, J. Mech. Behav.
Biomed. Mater. 1 (2008) 153–164.
I. BIOMECHANICS