Page 306 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 306
Ecofuel conversion technology of inedible lipid feedstocks to renewable fuel 263
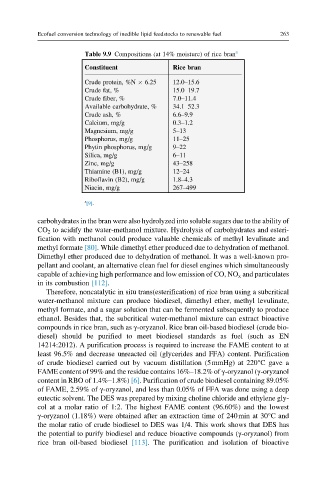
Table 9.9 Compositions (at 14% moisture) of rice bran a
Constituent Rice bran
Crude protein, %N 6.25 12.0–15.6
Crude fat, % 15.0–19.7
Crude fiber, % 7.0–11.4
Available carbohydrate, % 34.1–52.3
Crude ash, % 6.6–9.9
Calcium, mg/g 0.3–1.2
Magnesium, mg/g 5–13
Phosphorus, mg/g 11–25
Phytin phosphorus, mg/g 9–22
Silica, mg/g 6–11
Zinc, mg/g 43–258
Thiamine (B1), mg/g 12–24
Riboflavin (B2), mg/g 1.8–4.3
Niacin, mg/g 267–499
a
[9].
carbohydrates in the bran were also hydrolyzed into soluble sugars due to the ability of
CO 2 to acidify the water-methanol mixture. Hydrolysis of carbohydrates and esteri-
fication with methanol could produce valuable chemicals of methyl levulinate and
methyl formate [80]. While dimethyl ether produced due to dehydration of methanol.
Dimethyl ether produced due to dehydration of methanol. It was a well-known pro-
pellant and coolant, an alternative clean fuel for diesel engines which simultaneously
capable of achieving high performance and low emission of CO, NO x and particulates
in its combustion [112].
Therefore, noncatalytic in situ trans(esterification) of rice bran using a subcritical
water-methanol mixture can produce biodiesel, dimethyl ether, methyl levulinate,
methyl formate, and a sugar solution that can be fermented subsequently to produce
ethanol. Besides that, the subcritical water-methanol mixture can extract bioactive
compounds in rice bran, such as γ-oryzanol. Rice bran oil-based biodiesel (crude bio-
diesel) should be purified to meet biodiesel standards as fuel (such as EN
14214:2012). A purification process is required to increase the FAME content to at
least 96.5% and decrease unreacted oil (glycerides and FFA) content. Purification
of crude biodiesel carried out by vacuum distillation (5mmHg) at 220°C gave a
FAME content of 99% and the residue contains 16%–18.2% of γ-oryzanol (γ-oryzanol
content in RBO of 1.4%–1.8%) [6]. Purification of crude biodiesel containing 89.05%
of FAME, 2.59% of γ-oryzanol, and less than 0.05% of FFA was done using a deep
eutectic solvent. The DES was prepared by mixing choline chloride and ethylene gly-
col at a molar ratio of 1:2. The highest FAME content (96.60%) and the lowest
γ-oryzanol (1.18%) were obtained after an extraction time of 240min at 30°C and
the molar ratio of crude biodiesel to DES was 1/4. This work shows that DES has
the potential to purify biodiesel and reduce bioactive compounds (γ-oryzanol) from
rice bran oil-based biodiesel [113]. The purification and isolation of bioactive