Page 408 - Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
P. 408
362 Advances in Eco-Fuels for a Sustainable Environment
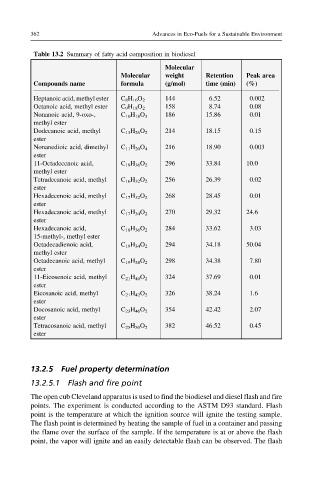
Table 13.2 Summary of fatty acid composition in biodiesel
Molecular
Molecular weight Retention Peak area
Compounds name formula (g/mol) time (min) (%)
Heptanoic acid, methyl ester C 8 H 16 O 2 144 6.52 0.002
Octanoic acid, methyl ester C 9 H 18 O 2 158 8.74 0.08
Nonanoic acid, 9-oxo-, C 10 H 18 O 3 186 15.86 0.01
methyl ester
Dodecanoic acid, methyl C 13 H 26 O 2 214 18.15 0.15
ester
Nonanedioic acid, dimethyl C 11 H 20 O 4 216 18.90 0.003
ester
11-Octadecenoic acid, C 19 H 36 O 2 296 33.84 10.0
methyl ester
Tetradecanoic acid, methyl C 16 H 32 O 2 256 26.39 0.02
ester
Hexadecenoic acid, methyl C 17 H 32 O 2 268 28.45 0.01
ester
Hexadecanoic acid, methyl C 17 H 34 O 2 270 29.32 24.6
ester
Hexadecanoic acid, C 18 H 36 O 2 284 33.62 3.03
15-methyl-, methyl ester
Octadecadienoic acid, C 19 H 34 O 2 294 34.18 50.04
methyl ester
Octadecanoic acid, methyl C 19 H 38 O 2 298 34.38 7.80
ester
11-Eicosenoic acid, methyl C 21 H 40 O 2 324 37.69 0.01
ester
Eicosanoic acid, methyl C 21 H 42 O 2 326 38.24 1.6
ester
Docosanoic acid, methyl C 23 H 46 O 2 354 42.42 2.07
ester
Tetracosanoic acid, methyl C 25 H 50 O 2 382 46.52 0.45
ester
13.2.5 Fuel property determination
13.2.5.1 Flash and fire point
The open cub Cleveland apparatus is used to find the biodiesel and diesel flash and fire
points. The experiment is conducted according to the ASTM D93 standard. Flash
point is the temperature at which the ignition source will ignite the testing sample.
The flash point is determined by heating the sample of fuel in a container and passing
the flame over the surface of the sample. If the temperature is at or above the flash
point, the vapor will ignite and an easily detectable flash can be observed. The flash