Page 111 - Advances in Forensic Applications of Mass Spectrometry - Jehuda Yinon
P. 111
1522_C02.fm Page 96 Wednesday, November 12, 2003 9:36 AM
298 367 494 491
271 446 312 324 528
450
Norm.
2000000
Abundance IS
0
3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 5.5 6.0 Time (min)
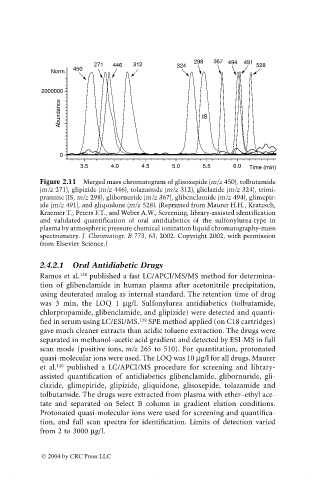
Figure 2.11 Merged mass chromatogram of glisoxepide (m/z 450), tolbutamide
(m/z 271), glipizide (m/z 446), tolazamide (m/z 312), gliclazide (m/z 324), trimi-
pramine (IS, m/z 298), glibornuride (m/z 367), glibenclamide (m/z 494), glimepir-
ide (m/z 491), and gliquidone (m/z 528). (Reprinted from Maurer H.H., Kratzsch,
Kraemer T., Peters F.T., and Weber A.W., Screening, library-assisted identification
and validated quantification of oral antidiabetics of the sulfonylurea-type in
plasma by atmospheric pressure chemical ionization liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 773, 63, 2002. Copyright 2002, with permission
from Elsevier Science.)
2.4.2.1 Oral Antidiabetic Drugs
138
Ramos et al. published a fast LC/APCI/MS/MS method for determina-
tion of glibenclamide in human plasma after acetonitrile precipitation,
using deuterated analog as internal standard. The retention time of drug
was 3 min, the LOQ 1 mg/l. Sulfonylurea antidiabetics (tolbutamide,
chlorpropamide, glibenclamide, and glipizide) were detected and quanti-
139
fied in serum using LC/ESI/MS. SPE method applied (on C18 cartridges)
gave much cleaner extracts than acidic toluene extraction. The drugs were
separated in methanol–acetic acid gradient and detected by ESI-MS in full
scan mode (positive ions, m/z 265 to 510). For quantitation, protonated
quasi-molecular ions were used. The LOQ was 10 mg/l for all drugs. Maurer
140
et al. published a LC/APCI/MS procedure for screening and library-
assisted quantification of antidiabetics glibenclamide, glibornuride, gli-
clazide, glimepiride, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide, tolazamide and
tolbutamide. The drugs were extracted from plasma with ether–ethyl ace-
tate and separated on Select B column in gradient elution conditions.
Protonated quasi-molecular ions were used for screening and quantifica-
tion, and full scan spectra for identification. Limits of detection varied
from 2 to 3000 mg/l.
© 2004 by CRC Press LLC