Page 94 - Advances in Renewable Energies and Power Technologies
P. 94
2. Criteria for Site Selection 67
Table 2.2 Associated Criteria for Selected Solar Photovoltaic Site
Suitability Studiesdcont’d
Criteria Subcriteria References
Social Public acceptance [9,16,20,28]
Effect on agriculture [10,16,49]
Employment and tourism [16]
Risk Political and economic risk [9,28]
Time delay risk [28]
Environmental risk [28]
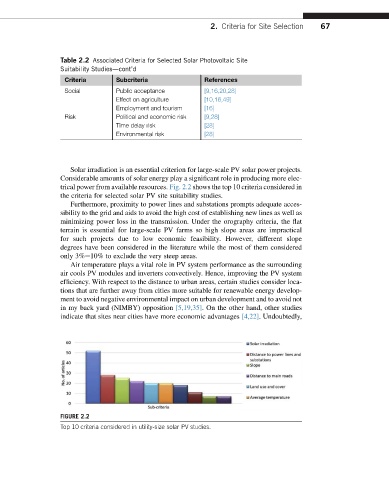
Solar irradiation is an essential criterion for large-scale PV solar power projects.
Considerable amounts of solar energy play a significant role in producing more elec-
trical power from available resources. Fig. 2.2 shows the top 10 criteria considered in
the criteria for selected solar PV site suitability studies.
Furthermore, proximity to power lines and substations prompts adequate acces-
sibility to the grid and aids to avoid the high cost of establishing new lines as well as
minimizing power loss in the transmission. Under the orography criteria, the flat
terrain is essential for large-scale PV farms so high slope areas are impractical
for such projects due to low economic feasibility. However, different slope
degrees have been considered in the literature while the most of them considered
only 3%e10% to exclude the very steep areas.
Air temperature plays a vital role in PV system performance as the surrounding
air cools PV modules and inverters convectively. Hence, improving the PV system
efficiency. With respect to the distance to urban areas, certain studies consider loca-
tions that are further away from cities more suitable for renewable energy develop-
ment to avoid negative environmental impact on urban development and to avoid not
in my back yard (NIMBY) opposition [5,19,35]. On the other hand, other studies
indicate that sites near cities have more economic advantages [4,22]. Undoubtedly,
FIGURE 2.2
Top 10 criteria considered in utility-size solar PV studies.