Page 63 - Aerodynamics for Engineering Students
P. 63
46 Aerodynamics for Engineering Students
a
Fig. 1.24 Lift curve for a thin aerofoil section with small nose radius of curvature
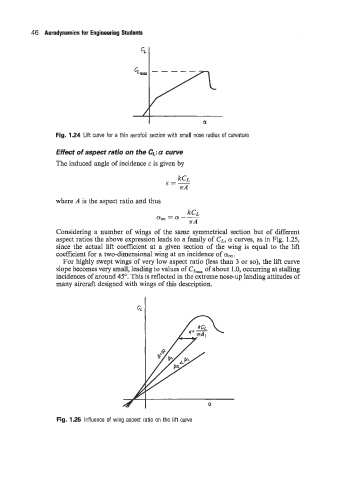
Effect of aspect ratio on the CL: a curve
The induced angle of incidence E is given by
where A is the aspect ratio and thus
Considering a number of wings of the same symmetrical section but of different
aspect ratios the above expression leads to a family of CL, a curves, as in Fig. 1.25,
since the actual lift coefficient at a given section of the wing is equal to the lift
coefficient for a two-dimensional wing at an incidence of am.
For highly swept wings of very low aspect ratio (less than 3 or so), the lift curve
slope becomes very small, leading to values of C,, of about 1.0, occurring at stalling
incidences of around 45". This is reflected in the extreme nose-up landing attitudes of
many aircraft designed with wings of this description.
CL I
Fig. 1.25 Influence of wing aspect ratio on the lift curve