Page 147 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 147
03_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 12:48 pm Page 126
126 José Renato Coury et al.
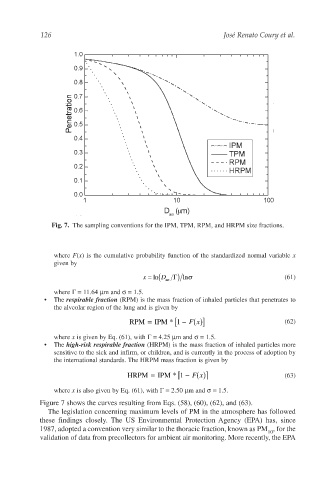
Fig. 7. The sampling conventions for the IPM, TPM, RPM, and HRPM size fractions.
where F(x) is the cumulative probability function of the standardized normal variable x
given by
x = ( D ae Γ ) lnσ (61)
ln
where Γ= 11.64 µm and σ= 1.5.
• The respirable fraction (RPM) is the mass fraction of inhaled particles that penetrates to
the alveolar region of the lung and is given by
RPM = IPM [ 1 − ( )] (62)
Fx
*
where x is given by Eq. (61), with Γ= 4.25 µm and σ= 1.5.
• The high-risk respirable fraction (HRPM) is the mass fraction of inhaled particles more
sensitive to the sick and infirm, or children, and is currently in the process of adoption by
the international standards. The HRPM mass fraction is given by
HRPM = IPM [ 1 − ( )] (63)
*
Fx
where x is also given by Eq. (61), with Γ= 2.50 µm and σ= 1.5.
Figure 7 shows the curves resulting from Eqs. (58), (60), (62), and (63).
The legislation concerning maximum levels of PM in the atmosphere has followed
these findings closely. The US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has, since
1987, adopted a convention very similar to the thoracic fraction, known as PM , for the
10
validation of data from precollectors for ambient air monitoring. More recently, the EPA