Page 331 - Air Pollution Control Engineering
P. 331
06_chap_wang.qxd 05/05/2004 4:10 pm Page 310
310 Lawrence K. Wang et al.
Table 1
Coolant Selection
Required condensation b Coolant inlet
a
temperature, T (ºF) Coolant temperature, T (ºF)
con cool,i
c T : 60–80 Water T − 15
con con
60 > T > 45 Chilled water T − 15
con con
45 >T ≥−30 Brine solutions (e.g., calcium chloride, T − 15
con con
Ethylene glycol)
−30 > T ≥−90 Chlorofluorocarbons (e.g., Freon-12) T − 15
con con
a Also emission stream outlet temperature.
b Assume the approach as 15ºF.
c Summer limit.
Source: ref. 4.
and the condenser’s removal efficiency. Dehumidification eliminates icing by using a
heat exchanger to cool the vapor to about 35ºF, prior to the condenser. Even with dehu-
midification, water vapor can remain a problem for subzero condensation systems,
requiring provisions such as dual condensers, in which heated air melts ice from the
off-line condenser (12).
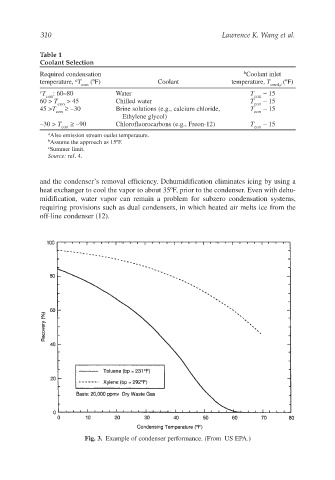
Fig. 3. Example of condenser performance. (From US EPA.)