Page 289 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 289
266 9 In-combustion Air Emission Control
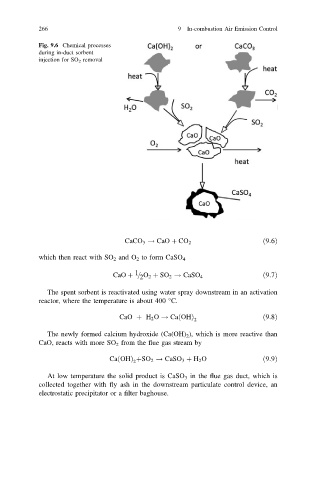
Fig. 9.6 Chemical processes
during in-duct sorbent
injection for SO 2 removal
CaCO 3 ! CaO þ CO 2 ð9:6Þ
which then react with SO 2 and O 2 to form CaSO 4
1
2
CaO þ = O 2 þ SO 2 ! CaSO 4 ð9:7Þ
The spent sorbent is reactivated using water spray downstream in an activation
reactor, where the temperature is about 400 °C.
CaO þ H 2 O ! Ca OHð Þ ð9:8Þ
2
The newly formed calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH) 2 ), which is more reactive than
CaO, reacts with more SO 2 from the flue gas stream by
Ca OHÞ þSO 2 ! CaSO 3 þ H 2 O ð9:9Þ
ð
2
At low temperature the solid product is CaSO 3 in the flue gas duct, which is
collected together with fly ash in the downstream particulate control device, an
electrostatic precipitator or a filter baghouse.