Page 292 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 292
9.4 In-combustion NO x Control 269
Fuel and transport
air Primary zone Secondary zone
Primary air
Secondary
air
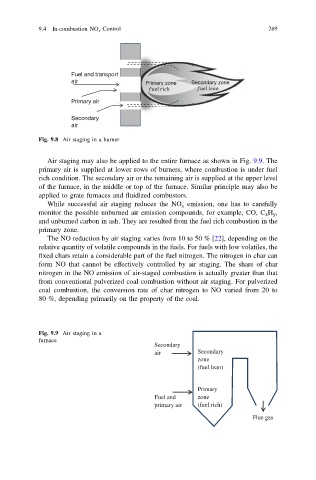
Fig. 9.8 Air staging in a burner
Air staging may also be applied to the entire furnace as shown in Fig. 9.9. The
primary air is supplied at lower rows of burners, where combustion is under fuel
rich condition. The secondary air or the remaining air is supplied at the upper level
of the furnace, in the middle or top of the furnace. Similar principle may also be
applied to grate furnaces and fluidized combustors.
While successful air staging reduces the NO x emission, one has to carefully
monitor the possible unburned air emission compounds, for example, CO, C x H y ,
and unburned carbon in ash. They are resulted from the fuel rich combustion in the
primary zone.
The NO reduction by air staging varies from 10 to 50 % [22], depending on the
relative quantity of volatile compounds in the fuels. For fuels with low volatiles, the
fixed chars retain a considerable part of the fuel nitrogen. The nitrogen in char can
form NO that cannot be effectively controlled by air staging. The share of char
nitrogen in the NO emission of air-staged combustion is actually greater than that
from conventional pulverized coal combustion without air staging. For pulverized
coal combustion, the conversion rate of char nitrogen to NO varied from 20 to
80 %, depending primarily on the property of the coal.
Fig. 9.9 Air staging in a
furnace
Secondary
air Secondary
zone
(fuel lean)
Primary
Fuel and zone
primary air (fuel rich)
Flue gas