Page 294 - Air pollution and greenhouse gases from basic concepts to engineering applications for air emission control
P. 294
9.4 In-combustion NO x Control 271
The reduction of NO x formation also depends on the unit size and the integration
of the burners with the furnace. There are three important types of low-NO x burners
that are integrated in pulverized coal combustion processes. They are,
• wall firing,
• tangentially firing
• opposed wall firing
Each of them may be dry bottom firing and wet bottom firing, where the bottom
ash is taken out in solid or liquid form, respectively. The former is preferred for
high ash-content fuels. The well-known cyclone furnace is a special case of wet
bottom firing furnaces [15].
9.4.3 Flue Gas Recirculation
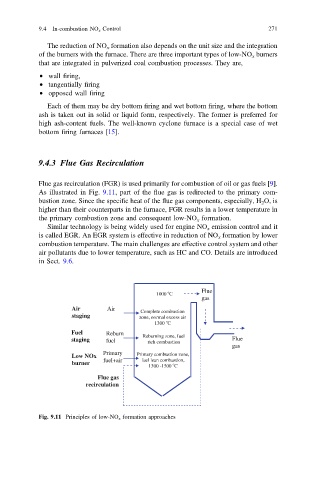
Flue gas recirculation (FGR) is used primarily for combustion of oil or gas fuels [9].
As illustrated in Fig. 9.11, part of the flue gas is redirected to the primary com-
bustion zone. Since the specific heat of the flue gas components, especially, H 2 O, is
higher than their counterparts in the furnace, FGR results in a lower temperature in
the primary combustion zone and consequent low-NO x formation.
Similar technology is being widely used for engine NO x emission control and it
is called EGR. An EGR system is effective in reduction of NO x formation by lower
combustion temperature. The main challenges are effective control system and other
air pollutants due to lower temperature, such as HC and CO. Details are introduced
in Sect. 9.6.
Flue
o
1000 C
gas
Air Air
Complete combustion
staging zone, normal excess air
o
1300 C
Fuel Reburn Reburning zone, fuel
staging fuel rich combustion Flue
gas
Primary Primary combustion zone,
Low NOx
burner fuel+air fuel lean combustion,
o
1300 -1500 C
Flue gas
recirculation
Fig. 9.11 Principles of low-NO x formation approaches