Page 119 - Algorithm Collections for Digital Signal Processing Applications using MATLAB
P. 119
3. Numerical Linear Algebra 107
U 6=68.0000 - 0.0000i
37.0000 - 0.0000i
20.0000 - 0.0000i
th
Therefore 6 term is 20 as expected (see the sequence).
8. COMPUTATION OF EXPONENTIAL
OF THE MATRIX
Let A be the matrix, which can be diagonalizable using Eigen matrix as
A
-1
A=EDE . e can be computed using series expansion as given below.
A
3
2
e = I + A +(A )/2! +(A )/3!+…..
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
-1
= I +EDE +(EDE EDE ) /2! +(EDE EDE EDE )/3!+…
3 -1
-1
0 -1
2 -1
= ED E +EDE + (ED E )/2! +(ED E )/3! +…
4
-1
2
0
3
= E[D + (D/1! )+(D /2!) + (D /3!) +(D /4!) +…] E
-1
D
= E e E
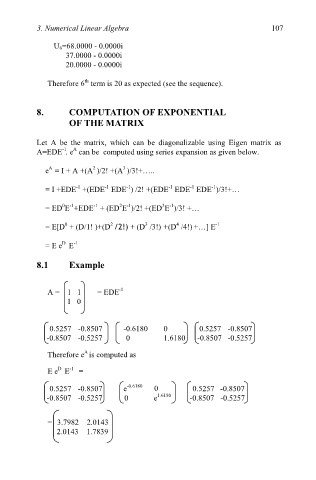
8.1 Example
-1
A = 1 1 = EDE
1 0
0.5257 -0.8507 -0.6180 0 0.5257 -0.8507
-0.8507 -0.5257 0 1.6180 -0.8507 -0.5257
A
Therefore e is computed as
D
E e E -1 =
0
0.5257 -0.8507 e -0.6180 0.5257 -0.8507
-
-0.8507 -0.5257 0 e 1.6180 0.8507 0.5257
-
= 3.7982 2.0143
2.0143 1.7839