Page 302 - Alternative Energy Systems in Building Design
P. 302
276 WIND ENERGY TECHNOLOGIES
Basics of Wind Turbine Operation
A wind energy system transforms the kinetic energy of the wind into mechanical or
electrical energy that can be harnessed for practical use. Mechanical energy is most
commonly used for pumping water in rural or remote locations. The farm windmill,
still seen in many rural areas of the United States, is a mechanical wind pump, but it
also can be used for many other purposes (e.g., grinding grain, sawing). Wind electric
turbines generate electricity for homes, businesses, and state utilities.
There are two basic designs in wind electric turbines: vertical-axis (11 eggbeater-
style blades) and horizontal-axis (propeller-style blades) machines. Horizontal-axis
wind turbines are most common today, constituting nearly all the utility-scale (100-kW
capacity and larger) turbines in the global market. Turbine system components include
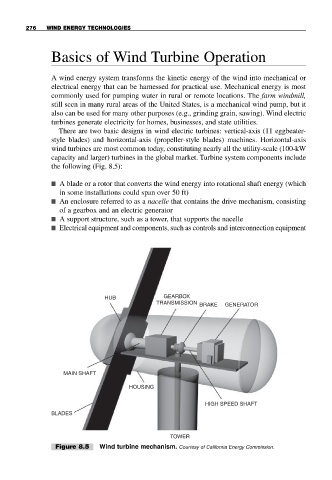
the following (Fig. 8.5):
■ A blade or a rotor that converts the wind energy into rotational shaft energy (which
in some installations could span over 50 ft)
■ An enclosure referred to as a nacelle that contains the drive mechanism, consisting
of a gearbox and an electric generator
■ A support structure, such as a tower, that supports the nacelle
■ Electrical equipment and components, such as controls and interconnection equipment
HUB GEARBOX
TRANSMISSION
BRAKE GENERATOR
MAIN SHAFT
HOUSING
HIGH SPEED SHAFT
BLADES
TOWER
Figure 8.5 Wind turbine mechanism. Courtesy of California Energy Commission.