Page 138 - An Introduction to Analytical Atomic Spectrometry - L. Ebdon
P. 138
Page 122
scanned through the range allowing ions of consecutively higher m/z to pass through, the other ions
striking the quadrupole rods. In practice, the quadrupole is scanned in small steps, albeit very rapidly,
with a typical mass scan from 2 to 260 m/z taking less than 100 ms. Alternatively, the RF/DC voltage
may be adjusted to allow ions of any chosen m/z to pass, rather than performing a sequential scan,
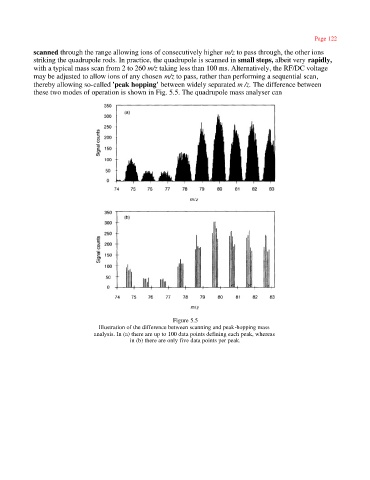
thereby allowing so-called 'peak hopping' between widely separated m /z. The difference between
these two modes of operation is shown in Fig. 5.5. The quadrupole mass analyser can
Figure 5.5
Illustration of the difference between scanning and peak-hopping mass
analysis. In (a) there are up to 100 data points defining each peak, whereas
in (b) there are only five data points per peak.