Page 272 -
P. 272
252 CHAPTER 5 LINEAR PROGRAMMING: THE SIMPLEX METHOD
14 Solve the following linear programme:
Min 3x 1 þ 4x 2 þ 8x 3
s:t:
4x 1 þ 2x 2 12
4x 2 þ 8x 3 16
x 1 ; x 2 ; x 3 0
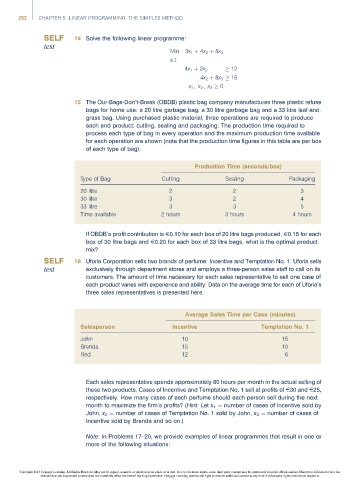
15 The Our-Bags-Don’t-Break (OBDB) plastic bag company manufactures three plastic refuse
bags for home use: a 20 litre garbage bag, a 30 litre garbage bag and a 33 litre leaf-and-
grass bag. Using purchased plastic material, three operations are required to produce
each end product: cutting, sealing and packaging. The production time required to
process each type of bag in every operation and the maximum production time available
for each operation are shown (note that the production time figures in this table are per box
of each type of bag).
Production Time (seconds/box)
Type of Bag Cutting Sealing Packaging
20 litre 2 2 3
30 litre 3 2 4
33 litre 3 3 5
Time available 2 hours 3 hours 4 hours
If OBDB’s profit contribution is E0.10 for each box of 20 litre bags produced, E0.15 for each
box of 30 litre bags and E0.20 for each box of 33 litre bags, what is the optimal product
mix?
16 Uforia Corporation sells two brands of perfume: Incentive and Temptation No. 1. Uforia sells
exclusively through department stores and employs a three-person sales staff to call on its
customers. The amount of time necessary for each sales representative to sell one case of
each product varies with experience and ability. Data on the average time for each of Uforia’s
three sales representatives is presented here.
Average Sales Time per Case (minutes)
Salesperson Incentive Temptation No. 1
John 10 15
Brenda 15 10
Red 12 6
Each sales representative spends approximately 80 hours per month in the actual selling of
these two products. Cases of Incentive and Temptation No. 1 sell at profits of E30 and E25,
respectively. How many cases of each perfume should each person sell during the next
month to maximize the firm’s profits? (Hint: Let x 1 ¼ number of cases of Incentive sold by
John, x 2 ¼ number of cases of Temptation No. 1 sold by John, x 3 ¼ number of cases of
Incentive sold by Brenda and so on.)
Note: In Problems 17–20, we provide examples of linear programmes that result in one or
more of the following situations:
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.