Page 304 -
P. 304
284 CHAPTER 7 TRANSPORTATION, ASSIGNMENT AND TRANSSHIPMENT PROBLEMS
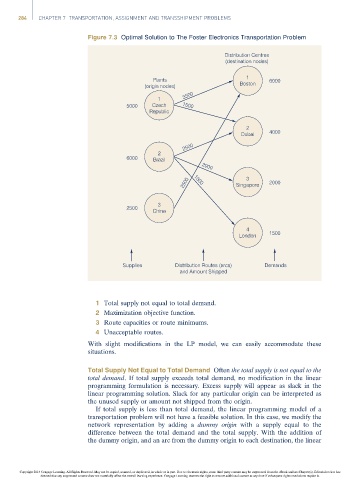
Figure 7.3 Optimal Solution to The Foster Electronics Transportation Problem
Distribution Centres
(destination nodes)
Plants 1 6000
(origin nodes) Boston
3500
1
5000 Czech 1500
Republic
2
Dubai 4000
2500
2
6000 Brazil
2000
3
2500 1500 Singapore 2000
3
2500
China
4
London 1500
Supplies Distribution Routes (arcs) Demands
and Amount Shipped
1 Total supply not equal to total demand.
2 Maximization objective function.
3 Route capacities or route minimums.
4 Unacceptable routes.
With slight modifications in the LP model, we can easily accommodate these
situations.
Total Supply Not Equal to Total Demand Often the total supply is not equal to the
total demand. If total supply exceeds total demand, no modification in the linear
programming formulation is necessary. Excess supply will appear as slack in the
linear programming solution. Slack for any particular origin can be interpreted as
the unused supply or amount not shipped from the origin.
If total supply is less than total demand, the linear programming model of a
transportation problem will not have a feasible solution. In this case, we modify the
network representation by adding a dummy origin with a supply equal to the
difference between the total demand and the total supply. With the addition of
the dummy origin, and an arc from the dummy origin to each destination, the linear
Copyright 2014 Cengage Learning. All Rights Reserved. May not be copied, scanned, or duplicated, in whole or in part. Due to electronic rights, some third party content may be suppressed from the eBook and/or eChapter(s). Editorial review has
deemed that any suppressed content does not materially affect the overall learning experience. Cengage Learning reserves the right to remove additional content at any time if subsequent rights restrictions require it.